Figure 4 – The fate of free mADPr.
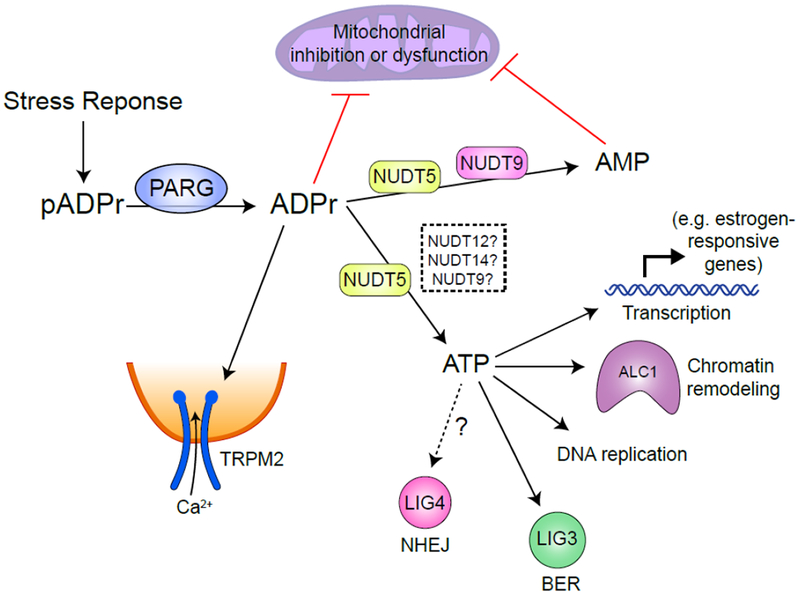
Following a stress response, a large pool of free mADPr is generated by PARP and PARG catalyzed PAR polymerization and degradation in the nucleus. Free mADPr activates TRPM2 cation channel, inducing Ca2+ influx into cells (84). NUDT9 catalyzes mADPr to AMP (91), while NUDT5 possess two catalytical activities to convert mADPr to either AMP or ATP (94). Over-production of mADPr or AMP can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction (92). ATP generated by NUDT5 (whether other Nudix family proteins also catalyze this process is undetermined) may be used locally for transcription, chromatin remodeling during DNA replication or repair.
