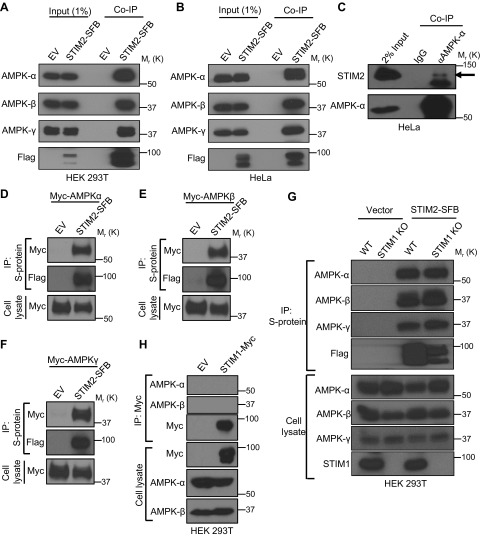
Figure 1 .
STIM2 interacts with AMPK. A, B) Coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of STIM2 and AMPK subunits in HEK 293T (A) and HeLa (B) cells. Protein extracts from cells stably expressing STIM2-SFB were immunoprecipitated using S-protein beads after immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Cells expressing empty vector (EV) were used as the control. C) Endogenous interaction of STIM2 and AMPK. HeLa cell lysates were subjected for immunoprecipitation using mouse anti–AMPK-α antibody and IgG control. Coprecipitated STIM2 was detected after immunoblotting. The arrow denotes STIM2 in AMPK immunoprecipitation. D–F) STIM2 interacts with all 3 subunits of AMPK. HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with STIM2-SFB or EV along with myc–AMPK-α (D), myc–AMPK-β (E), or myc–AMPK-γ (F), and then subjected for STIM2-SFB immunoprecipitation. Coprecipitated proteins were detected by immunoblotting with anti-myc antibody. G) STIM2 interacts with AMPK independent of STIM1. STIM1 wild-type (WT) or knock-out (KO) cells expressing STIM2-SFB or control vector were immunoprecipitated with S-protein beads. Coprecipitated proteins were probed by indicated antibodies. H) STIM1 does not interact with AMPK. Protein extracts from transiently transfected HEK293T cells with STIM1-myc were immunoprecipitated using S-protein beads after immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Cells expressing EV were used as control.