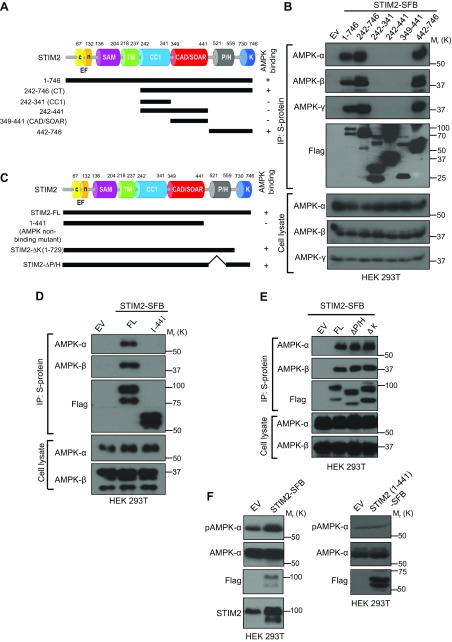
Figure 2 .
STIM2 interaction with AMPK promotes AMPK activation. A) Schematic representation of STIM2 full-length (FL) and deletion mutants used in this study. B) STIM2 interacts with AMPK through its C-terminal region. Protein extracts of HEK 293T cells expressing FL and truncated mutants of STIM2 were immunoprecipitated with S-protein beads and analyzed for coprecipitated AMPK subunits after immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. C) Schematic representation of STIM2 FL and other deletion mutants in this study. D) HEK 293T cells expressing STIM2 FL (1–746) and STIM2 1–441 were immunoprecipitated using S-protein beads and analyzed for coprecipitated proteins using the indicated antibodies. E) HEK 293T cells expressing FL STIM2, STIM2 deletion mutants for the P/H domain (∆P/H) or the K domain (∆K) were immunoprecipitated using S-protein beads and analyzed for coprecipitated proteins using indicated antibodies. F) Transient overexpression of STIM2 FL, but not its AMPK-nonbinding mutant, promotes AMPK phosphorylation. Cell lysates from HEK 293T cells expressing either empty vector, STIM2 FL, or its AMPK-nonbinding mutant (STIM2 1–441) were analyzed by immunoblotting for the phosphorylated and total levels of AMPK.