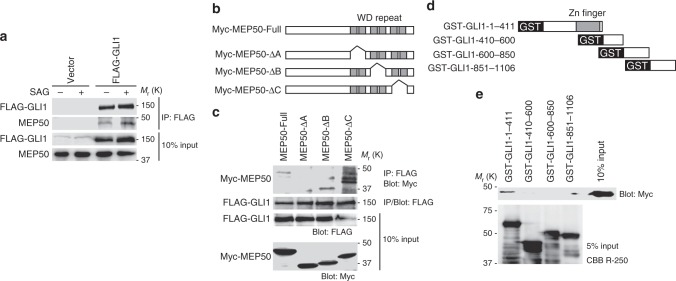
Fig. 1.
GLI1 interacts with the MEP50/PRMT5 complex. a FLAG-GLI1 interacted with endogenous MEP50 and interaction of FLAG-GLI1 and MEP50 was increased by HH signalling pathway activation. C3H10T1/2 cells were transfected with FLAG-GLI1 or the empty vector for 24 h and then treated with 300 nM SAG for an additional 24 h. Interaction of FLAG-GLI1 and MEP50 was detected by immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody followed by immunoblot analysis using anti-FLAG and anti-MEP50 antibodies. b Schematic structures of MEP50 deletion mutants. c Mapping of the GLI1-binding region in MEP50 by immunoprecipitation analysis. HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc-MEP50 deletion mutants and FLAG-GLI1 plasmids for 24 h. Interaction of FLAG-GLI1 and Myc-MEP50 deletion mutants was detected by immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody followed by immunoblot analysis using anti-FLAG and anti-Myc antibodies. d Schematic of GLI1 deletion mutants. e GST pull-down assays to map the MEP50-binding region in GLI1. GST-GLI1 deletion mutants coupled to glutathione sepharose were incubated with immunoprecipitated Myc-MEP50 from HEK293T cells. Immunoblotting was performed with an anti-Myc antibody. In a and e, data represent one of three independent experiments with similar results. In c, data represent one of two independent experiments with similar results. Unprocessed original scans of blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 6