Fig. 4.
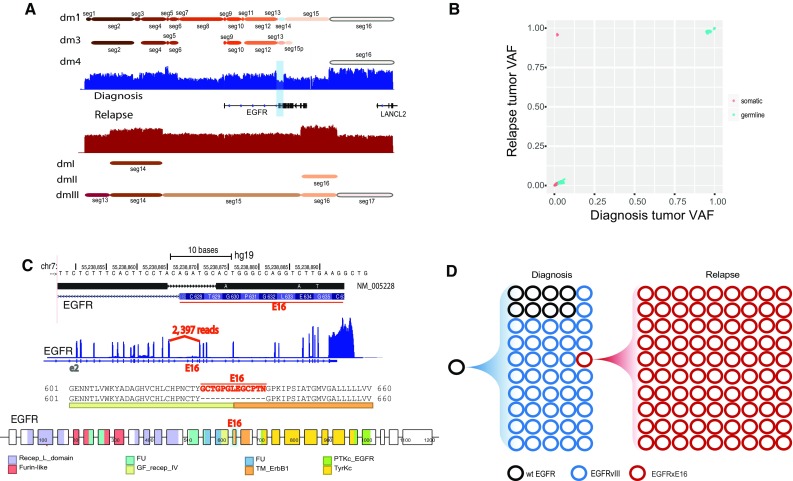
Characterization and evolution of the shared double minutes between the diagnosis and relapse samples of SJHGG019. a Highly amplified segments around EGFR are involved in multiple double minutes in both samples. Seg14 deleted in dm1 results in EGFRvIII. b Variant allele frequency comparison of the SNVs shared by dm1-specific segments in the diagnosis sample and dmIII-specific segments in the relapse sample. On the upper left corner are four somatic SNVs with low frequency (0.02) in the diagnosis sample and high frequency (0.96) in the relapse sample. c Among the four somatic SNVs, three are located close to each other on exon 16 of EGFR. Along with these three SNVs is an eight base pair deletion that disrupts the intron15/exon16 splicing acceptor site, leading to skipping of exon 16 in the EGFR RNA transcript, indicated by the missing coverage of exon16 in RNA-seq coverage track and large number of supporting reads for the novel splice junction. Consequently, the skipping of exon 16 produces an EGFR protein product with an in-frame deletion of 13-amino acids (GCTGPGLEGCPTN), which partially code for two protein domains: growth factor receptor domain IV (GF_recep_IV) and transmembrane ERBB1 like domain (TM_ErbB1). d Evolution of the EGFR-containing double minutes from diagnosis (dm1) to relapse (dmIII). Black circles represent double minutes carrying wild-type EGFR (wtEGFR), blue circles represent double minutes carrying EGFRvIII, and red circles represent double minutes carrying EGFR with exon 16 deletion in RNA transcript (EGFRxE16). The counts of circles in different colors reflect the relative abundance of each type of EGFR as estimated from sequencing data
