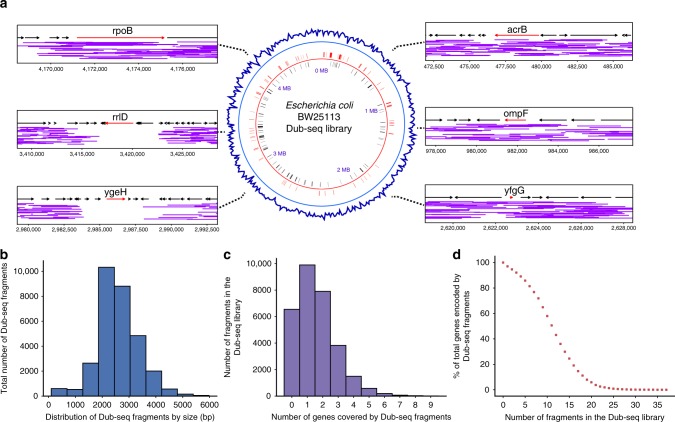
Fig. 2.
E. coli dual-barcoded shotgun expression library sequencing (Dub-seq) library characterization. a Center: genomic coverage of the E. coli BW25113 Dub-seq library in 10 kb windows (blue track). Black and red line-tracks represent genes essential for viability when deleted5 that are encoded on the negative and positive strands, respectively, and are covered in the Dub-seq library. Left and right: regions of the E. coli chromosome covering acrB, ompF, yfgG, ygeH, rrlD, and rpoB. Each purple line represents a Dub-seq genomic fragment (the y axis is random). b The fragment insert size distribution in the E. coli Dub-seq library. c The distribution of number of genes that are completely covered (start to stop codon) per genomic fragment in the E. coli Dub-seq library. d Cumulative distribution plot showing the percentage of genes in the E. coli genome (y axis) covered by a number of independent genomic fragments (x axis). Source data are provided as a Source Data file