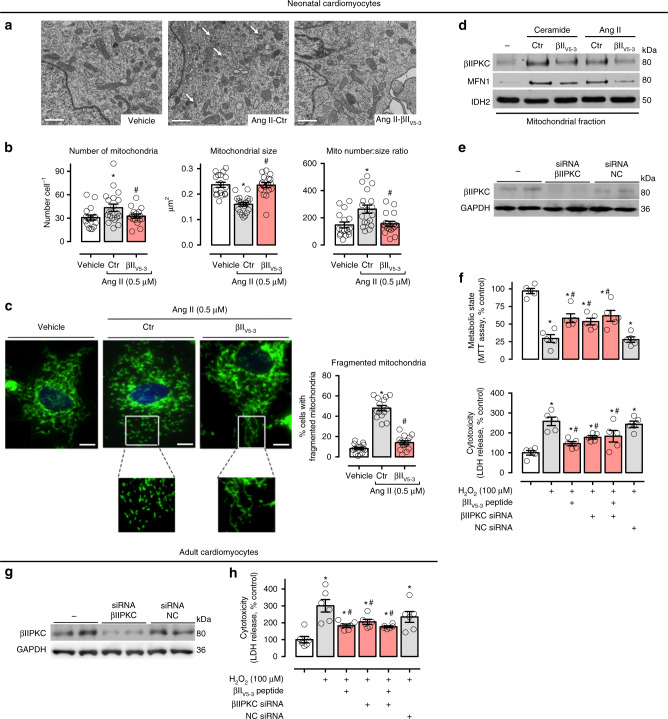
Fig. 2.
βIIPKC inhibition reduces mitochondrial fragmentation in cultured cardiomyocytes. a Representative transmission electron micrographs (white arrows indicate small mitochondria, scale bar: 1 μm) and b quantification of mitochondrial number and size in the transmission electron micrographs of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes in culture treated with TAT (carrier) or βIIV5-3 peptides for 30 min followed by incubation with angiotensin II (0.5 µM for 4 h, n = 5 per group). c Cells were then stained with anti-Tom20 antibody (green) and Hoechst stain and counted. Mitochondrial morphology was analyzed using a 63x oil immersion lens (scale bar: 5 μm). The analysis was done in a blinded fashion. The boxed area in each upper panel is enlarged under each micrograph. d Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes in culture were treated with TAT or βIIV5-3 peptides for 30 min followed by incubation with either C2-ceramide (40 μM) or angiotensin II (0.5 µM) for 4 h. After incubation, the mitochondrial levels of βIIPKC and Mfn1 were detected using specific antibodies (representative blot of three independent experiments). e Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes in culture were transfected with βIIPKC silence RNA (βIIPKC-siRNA) or control (NC-siRNA). f 48 h later cells were treated with TAT or βIIV5-3 peptides for 30 min followed by incubation with H2O2 (100 µM, 24 h). After incubation, cell viability and toxicity were measured by MTT assay and LDH release, respectively. g Adult rat cardiomyocytes in culture were transfected with βIIPKC-siRNA or NC-siRNA (n = 6 per group). h 24 h later cells were treated with TAT or βIIV5-3 peptides for 30 min followed by incubation with H2O2 (100 µM, 1 h). Cell toxicity was measured by LDH release. Data are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. control cells. #P < 0.05 vs. Ang II- or H2O2-treated cells. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post-hoc testing by Duncan