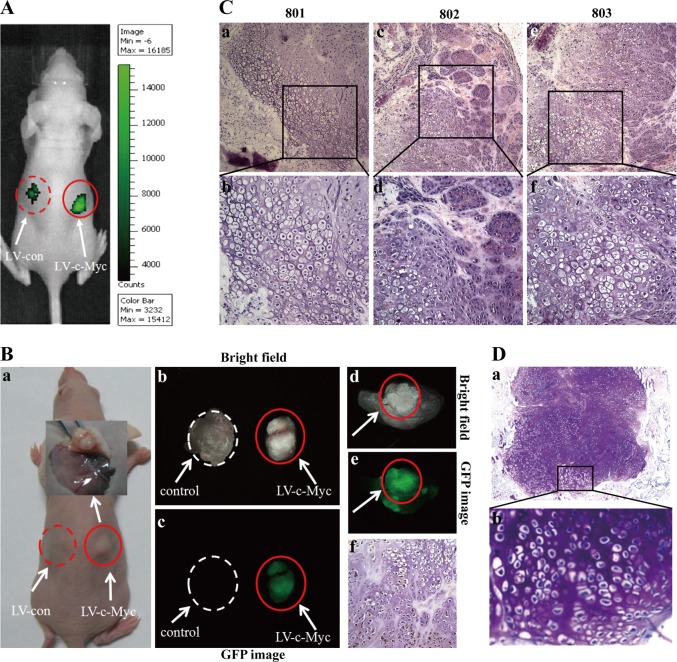
Fig. 2. In vivo cartilage-like tissue formation by c-Myc-expressing PEFs.
Vector and c-Myc-expressing PEFs were injected subcutaneously into the dorsal flank of nude mice (n = 5). The xenografts became palpable at sites injected with c-Myc-expressing PEFs 2 weeks after inoculation, and three out of five mice developed xenografts at the end of the experiment, whereas no xenografts were observed at sites injected with vector-expressing PEFs. a In vivo EGFP assay for the transplanted EGFP-positive vector-expressing PEFs (left) and c-Myc-expressing PEFs (right) at injected sites of nude mice by the IVIS Lumina Imaging System. b The suspected cartilage-like tissues developed from the transplanted c-Myc-expressing PEFs at injected sites (right) of a nude mouse (801). B-a Picture of a nude mouse (801) [shown in (A)] xenograft. B-b,c Assay of GFP expression in the xenograft stripped from a nude mouse (801) under stereo fluorescence microscope. Control tissues were obtained from the same nude mouse (801). B-d Picture of the cross section of GFP-positive graft harbouring LV-c-Myc [shown in (B-b,c; right)]. B-e GFP assay for the cross-section [shown in (B-d)] of a GFP-positive graft. B-f GFP-stained section of transplanted xenograft tissue formed by c-Myc-expressing PEFs. c HE staining of the suspected cartilage-like tissues formed from the transplanted c-Myc-expressing PEFs at injected sites of 3 nude mice (801, 802 and 803). Images (b, d and f) are higher magnifications of the rectangular regions indicated in images (a, c and e), respectively. Original magnification: 40×. d Toluidine blue staining of tissue sections shown in (c). b is a higher magnification of the rectangular region indicated in (a)