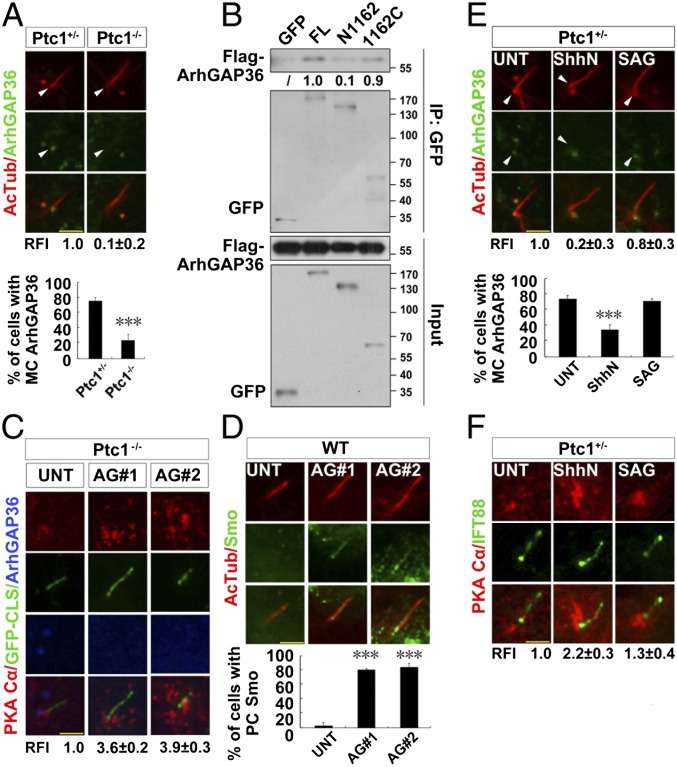
Fig. 3.
Removal of ciliary Ptc1 by Shh signaling abolishes centrosomal ArhGAP36 localization and increases the amount of centrosomal PKAc. (A) The mother centriolar (MC) localization of ArhGAP36 is impaired by Ptc1 knockout. G0 phase Ptc1+/− and Ptc1−/− cells were immunostained for the indicated proteins. Arrowheads indicate the MC localization of ArhGAP36. The RFIs and the ratio of MC-localized ArhGAP36 are shown Below each panel. (B) Ptc1 interacts with ArhGAP36 mainly via its C terminus. HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with the indicated plasmids, and arrested at the G0 phase, followed by an immunoprecipitation assay. The normalized results of immunoprecipitated Flag-ArhGAP36 by the indicated proteins are shown Below each panel; Flag-ArhGAP36 immunoprecipitated by full-length Ptc1-GFP was set as 1.0. (C) Knockdown of ArhGAP36 results in PKAc accumulation at the centrosome. The Ptc1−/− cells expressing a GFP-CLS sequence of Fibrocystin (53) were knocked down for ArhGAP36, arrested at the G0 phase, and immunostained for the indicated proteins. (D) Knockdown of ArhGAP36 results in Smo translocation to the ciliary proximal region. The WT cells were knocked down for ArhGAP36, arrested at the G0 phase, and immunostained for the indicated proteins. (E and F) Ptc1 inhibition by Shh signaling causes ArhGAP36 removal from the MC and PKAc accumulation at the centrosome. G0 phase Ptc1+/− cells after the indicated treatments were immunostained for the indicated proteins. Arrowheads indicate the MC localization of ArhGAP36. (Scale bars, 5 μm.) In the statistics histograms for results from A, D, and E, the values are the mean ± SD; 50 cells per sample were randomly selected and counted in each of three independent experiments. ***P < 0.001. The RFI results in A, C, E, and F are shown as the mean ± SD; 50 cells were randomly selected for calculation.