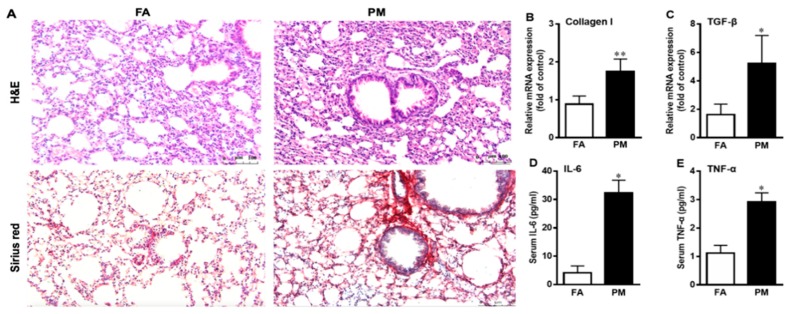
Figure 2.
PM2.5 exposure induces pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. (A) Lung sections from filtered air (FA) and particulate matter (PM2.5)-exposed mice were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Sirius red staining at 200× magnification. (B–E) After exposure for 12 weeks, the mRNA levels of fibrotic genes collagen I and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) in lungs (B,C) and the level of inflammatory factors interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in serum (D,E) were measured by qPCR and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits, respectively. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD); * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. FA group.