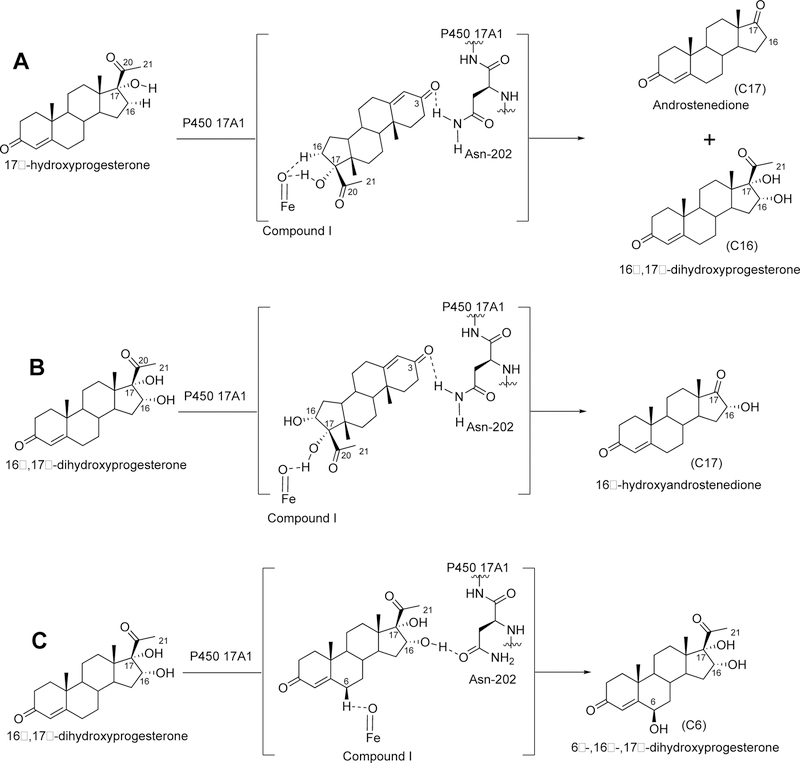
Figure 64.
New oxidation products of P450 17A1 detected with 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 16α-,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone. (A) P450 17A1 oxidizes 17α-hydroxyprogesterone to 16α,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone and androstenedione. (B) P450 17A1 cleaves the C17,C20-bond of 16α-,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone to yield 16α-hydroxyandrostenedione. (C) P450 17A1 hydroxylates 16α-,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone to afford 6β-,16α-,17α-trihydroxyprogesterone.238 In Parts A and B, Compound I is shown to abstract the hydrogen atom of the 17-hydroxy group of the substrate to yield the 19-carbon C17-C20 lyase products, but this C17-C20 lyase reaction can occur also from a nucleophilic attack of the 17-hydroxy group onto Compound I (see text for discussion). (C) A different orientation of the steroid in the enzyme active site is due to the hydrogen bonding interaction between the 16-hydroxy group with Asn-202.