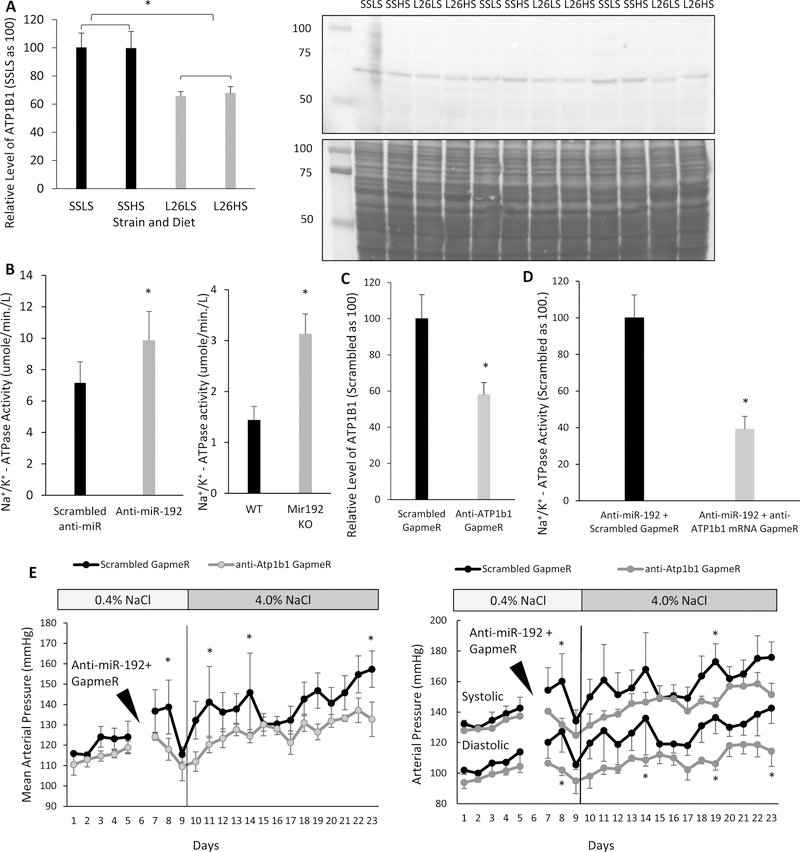
Figure 4. Atp1b1 targeting contributes to the protective effect of miR-192-5p against hypertension.
A. The level of ATP1B1 in the renal cortex was higher in SS than that in SS.13BN26 (L26) rats. Western blot signals of ATP1B1 were normalized by Coomassie blue staining of the membrane shown below the Western blot. n=3, *, p< 0.05. B. Na+/K+-ATPase activity in the renal cortex was increased in SS.13BN26 rats with intrarenal knockdown of miR-192-5p and in Mir192 KO mice at the end of the blood pressure experiment shown in Figure 3. n=5 Scrambled anti-miR and 6 anti-miR-192-5p; n=5 WT and 6 KO; *, p< 0.05. C. Anti-Atp1b1 GapmeR reduced the level of ATP1B1 based on Western blot analysis of the renal cortex. n=3*, p< 0.05. D. Anti-Atp1b1 GapmeR treatment reduced the activity of Na+/K+-ATPase. n=3, *, p< 0.05. E. Knockdown of ATP1B1 attenuated hypertension in L26 rats treated simultaneously with anti-miR-192-5p. Anti-miR-192 and anti-Atp1b1 GapmeR or scrambled GapmeR were administered by intrarenal artery injection at the time indicated. n=4, *, p< 0.05 between rats treated with anti-miR-192-5p and anti-Atp1b1 GapmeR and those treated with anti-miR-192-5p and scrambled GapmeR.