Figure 6 |. Hrr25-dependent Thr4 phosphorylation recruits RTT103.
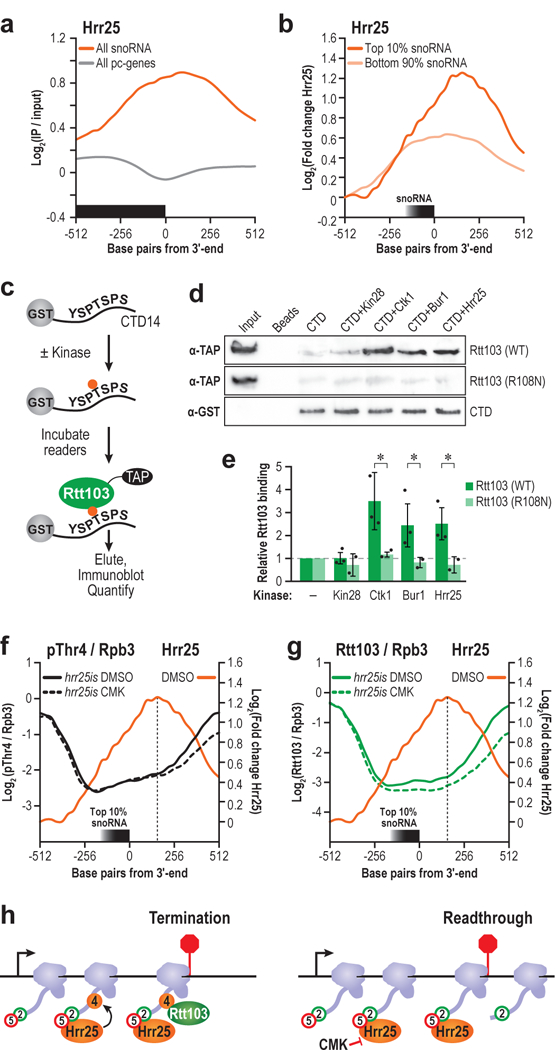
(a) Hrr25 ChIP centered at the 3ʹ end of snoRNA genes (orange) or protein coding genes (grey). (b) Hrr25 ChIP centered at the 3ʹ end of the snoRNAs with the top 10% 3ʹ extension indices (dark orange) or bottom 90% (light orange) (c) Schematic of assay used to confirm direct binding. (d) Rtt103 (WT) or Rtt103 (R108N) was incubated with kinase-treated or mock-treated beads, eluted, and analyzed via western blot. α-GST CTD loading control is shown. Input refers to unbound Rtt103, loaded at 10% the abundance of Rtt103 incubated with CTD. Full length blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 12. (e) Quantification of the fold change in Rtt103 vs. the beads only control for unphosphorylated CTD, or kinase-treated CTD is shown. (n=3 independent experiments, error bars are S.D., * p<0.05). (f) Profiles of pThr4 normalized to Rpb3 in hrr25is treated with either DMSO (solid black) or CMK (dotted black) at the snoRNAs with the highest 3ʹ extension indices. Hrr25 profile is overlaid (orange) (g) Similar profiles of Rtt103 in hrr25is treated with either DMSO (solid green) or CMK (dotted green), with the Hrr25 profile overlaid (orange). (h) Model of role of Hrr25 in terminating snoRNA genes. Arrow is TSS, and the red bar is the 3ʹ end. Hrr25 is recruited by pSer5 and pSer2 marks to phosphorylate Thr4. Rtt103 binds pThr4 and terminates transcription.
