Figure 2: rFGF21 reduced the permeability of cultured HBMEC monolayer after Hyperglycemia-IL1β (HG-IL1β) injury.
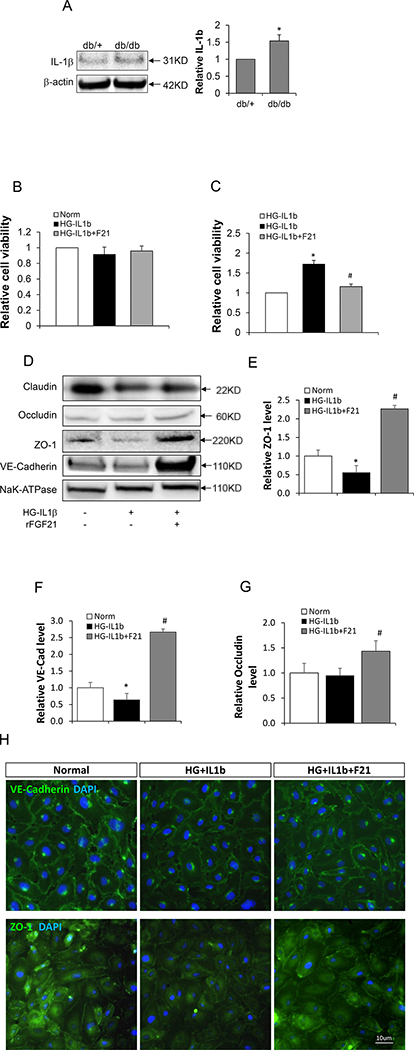
Cultured HBMEC monolayer treated with HG-IL1β was used to mimic BBB injury under diabetic conditions. The monolayer was then treated with rFGF21 and the permeability was measured. (A) IL-1β protein level in diabetic mice brain measured by Western blot (* p<0.05 vs. db/+, n=4); (B) Viability of cultured HBMEC after treatment with HG-IL1β and rFGF21; (C) Relative HBMEC monolayer permeability after treatment with HG-IL1β and rFGF21 (* p<0.05 vs. norm; # p<0.05 vs. HG-IL1β; n=6); (D) Representative western blot images of junction protein expression in cultured HBMEC after HG-IL1β and rFGF21 treatment; (E, F, G) Quantification of junction protein ZO-1, VE-cadherin and Occludin in cultured HBMEC (*p<0.05 vs. norm; # p<0.05 vs. HG-IL1β; n=6); (H) Immunocytochemistry of ZO-1 and VE-cadherin in cultured HBMEC after HG-IL1β and rFGF21 treatment.
