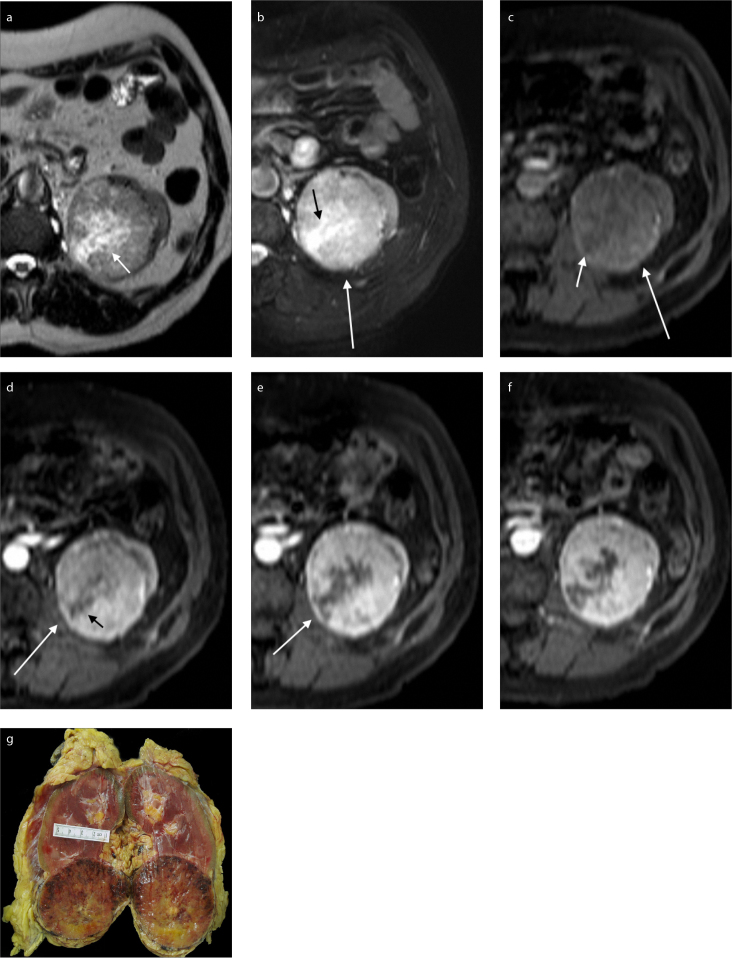
Figure 2. a–g.
A 62-year-old woman with a 76 mm mass in the right kidney diagnosed as chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Axial T2-weighted fast spin-echo image (a) shows that the renal mass has heterogeneous signal intensity and includes a hyperintense scar (arrow). In axial fat-saturated T2 image (b), the tumor is heterogeneous (white arrow) and scar is hyperintense (black arrow). In axial precontrast fat-saturated T1-weighted image (c), the tumor is isointense with renal cortex (long arrow) and the scar is hypointense (short arrow). Axial arterial phase fat-saturated gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted image (d) shows heterogeneous enhancement. There is a millimetric hypointense area at scar region (black arrow). The other parts of the lesion show slightly higher enhancement than renal cortex (white arrow). Parenchymal phase image (e) shows increased enhancement in tumor and hypointense scar (arrow). Parenchymal phase image (f) shows enhancement within the mass followed by washout (signal intensity ratio in arterial phase, 50.5; signal intensity ratio in parenchymal phase, 55.9; signal intensity ratio in excretory phase, 47.9; arterial phase wash-in value, 101.9; parenchymal phase wash-in value, 127.0; excretory phase wash-in value, 88.6; wash-out value [parenchymal], 12.5; wash-out value [excretory], −6.6). Gross specimen image (g) of the tumor.