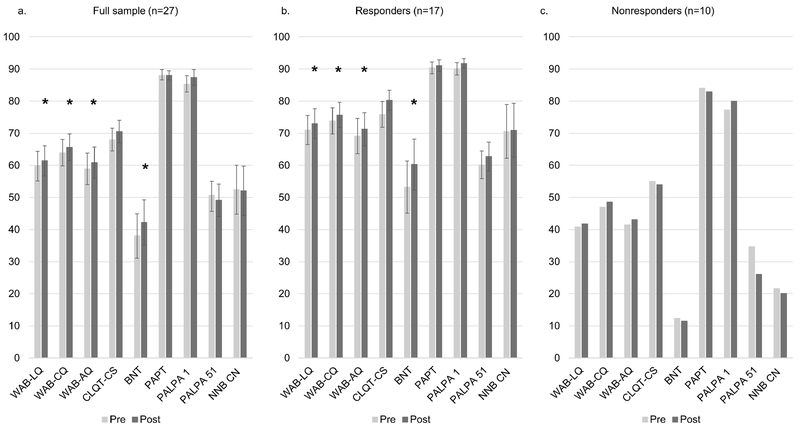
Figure 5:
Changes from pre- to post-treatment in average accuracy on standardized outcome measures of cognitive-linguistic function for the full sample (a), responder (b) and nonresponder (c) groups. Significant gains were seen on measures of global cognitive-linguistic functioning and naming ability post-treatment for the full-sample and responder group (* = significant at p < .05 level).
Note: WAB-LQ = Western Aphasia Battery-Language Quotient; WAB-CQ = WAB-Cortical Quotient; WAB-AQ = WAB-Aphasia Quotient; CLQT-CS = Cognitive Linguistic Quick Test-Composite Severity; BNT = Boston Naming Test; PAPT = Pyramids and Palm Trees Test; PALPA 1 = Same-Different Nonword Minimal Pair Task (auditory); PALPA 51 = Word Semantic Association (written); NNB CN = Northwestern Naming Battery-Confrontation Naming subtest