Figure 1:
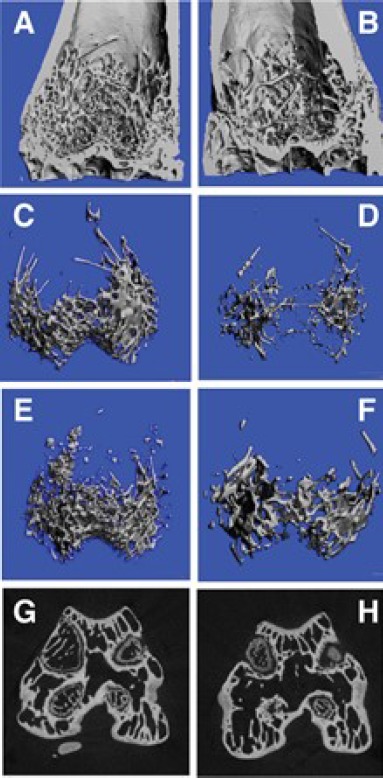
A - Section of Distal Femur of the Study Group showing dense trabeculae; B-Section of the Distal Femur of the Control Group sparse trabecular pattern; C-HRPQCT reconstruction of Trabecular Pattern of Distal Femur in Study Group indicating dense bony structure;D-HRPQCT reconstruction of Trabecular Pattern of Distal Femur in Control Group reveals wide trabecular spaces and empty areas; E-HRPQCT reconstruction of Trabecular Pattern of Distal Femur in Study Group of another animal showing high quantity and quality of the areas; F-HRPQCT reconstruction of Trabecular Pattern of Distal Femur in Control Group of another animal showing sparse bone; G - Saggital section of the distal femur in the study group showing the condyles filled with new bone with plenty of trabeculae; H - Saggital section of the distal femur in the control group showing wide spaces of no bone to minimal bone in the areas examined when compared to the study group.
