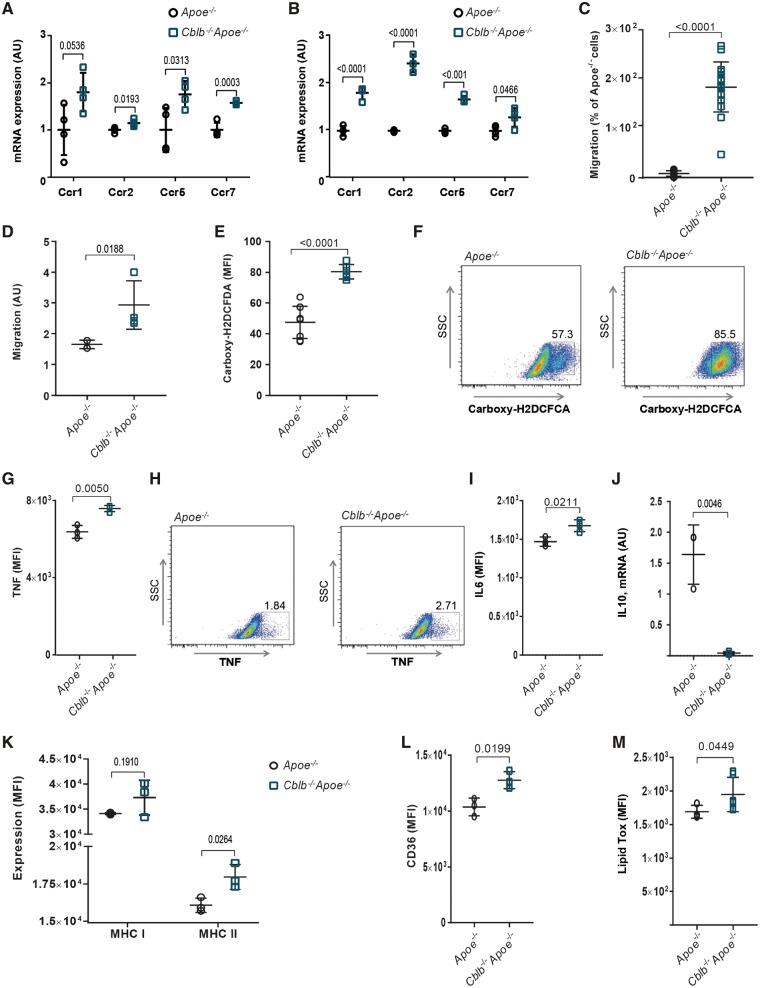
Figure 3.
Casitas B-cell lymphoma-B deficiency induces an atherogenic phenotype in macrophages. Quantification of mRNA expression of chemokine receptors CCR1, 2, 5, and 7 in monocytes (A) and bone marrow-derived macrophages (B) of Apoe−/− (n = 4) and Cblb−/−Apoe−/− (n = 4) mice. (C) CCL2-induced monocyte migration was increased in Cblb−/−Apoe−/− mice (n = 16 per genotype). (D) Migration of bone marrow-derived macrophages from Apoe−/− and Cblb−/−Apoe−/− mice towards 10 ng/mL MCP-1 by transwell assay (n = 3 experiments). (E, F) Flow cytometric analysis of reactive oxygen species production by Apoe−/− (n = 8) and Cblb−/−Apoe−/− (n = 6) bone marrow-derived macrophages after 48 h LPS stimulation. Representative dot plots; numbers indicate percentage of bone marrow-derived macrophages positive for carboxy-H2DCFCA. Representative dot plot and graph of TNF (G, H) and interleukin-6 (I) production after 24 h exposure to oxLDL (n = 3 experiments). (J) mRNA expression of interleukin-10 in bone marrow-derived macrophages from Apoe−/− and Cblb−/−Apoe−/− mice after 24 h exposure to oxLDL (n = 3 experiments). Flow cytometric analysis of MHC-I and MHC-II expression (K) and CD36 expression (L) of bone marrow-derived macrophages (n = 3 experiments). (M) Flow cytometric analysis of lipid uptake in bone marrow-derived macrophages (n = 6). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation.