Figure 9. Proposed binding scheme for CaM regulation of RyR2 with increasing levels of cytosolic Ca2+.
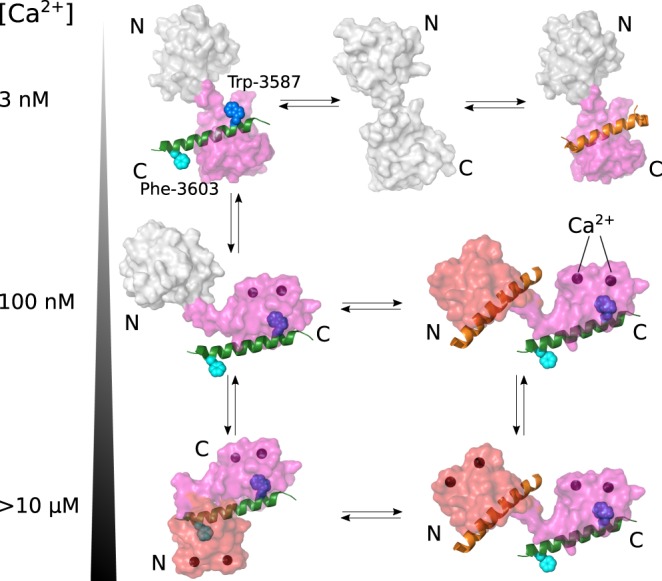
RyR2 CaMBD2 is indicated with a green α-helix and Ca2+ with dark spheres. When binding to RyR2, the CaM N-domain is highlighted in red and the C-domain in purple. Free domains are shown in white. At essentially Ca2+-free conditions (3 nM Ca2+, upper row), the CaM C-domain may bind to CaMBD2, involving Trp-3587, or to another RyR2 CaMBD (orange α-helix), such as CaMBD3. However, at resting cytosolic Ca2+ levels (∼100 nM, middle row), a Ca2+-saturated CaM C-domain binds to the CaMBD2 anchor residue, Trp-3587, and the apo-N-domain may interact with another CaMBD or may remain free. At cytosolic Ca2+ levels ∼1 µM and higher (illustrated as >10 µM, lower row), the CaM C-domain remains anchored to CaMBD2 Trp-3587, whereas the N-domain now binds Ca2+ and interacts with another site on RyR2 (e.g. CaMBD3), or clamps down on CaMBD2 Phe-3603.
