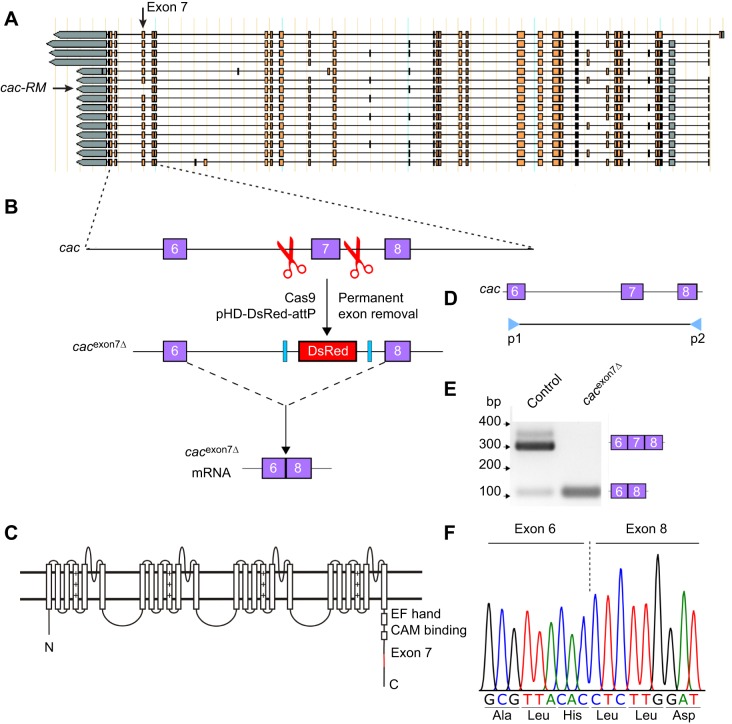
Fig. 1.
Generation of cacophony exon 7 deletion lines. (A) Predicted alternatively spliced cacophony transcripts from FlyBase, showing the position of exon 7 and that a single predicted isoform, cac-RM, lacks exon 7. (B) Schematic diagram showing the process of using CRISPR/Cas9 to delete exon 7 of cacophony. Cas9 was targeted to cut the genomic DNA on either side of exon 7, resulting in two double-stranded breaks, which were repaired via homologous recombination with a donor template containing DsRed, which was then incorporated into the genome. Splicing between exon 6 and 8 excludes the DsRed cassette, yielding cacexon7Δ mRNA. (C) Schematic diagram of the predicted cacophony protein, showing the location of exon 7 near the C-terminus. (D) Location of the primers in exon 6 and 8 used for RT-PCR to confirm the deletion of exon 7. (E) Representative DNA gel of the RT-PCR products from adult heads, showing a major 300 bp band that includes exon 7 and a minor 100 bp band lacking exon 7 from control animals. By contrast, RT-PCR from the cacexon7Δ line only yielded the 100 bp band. (F) Sequencing chromatogram resulting from the sequencing of the 100 bp band from the cacexon7Δ line showed that exon 6 splices directly to exon 8, excluding exon 7.