Fig. 1. The mechanisms of S6K1 inhibitors-induced feedback activation of the PI3K pathway and insulin receptor sensitization.
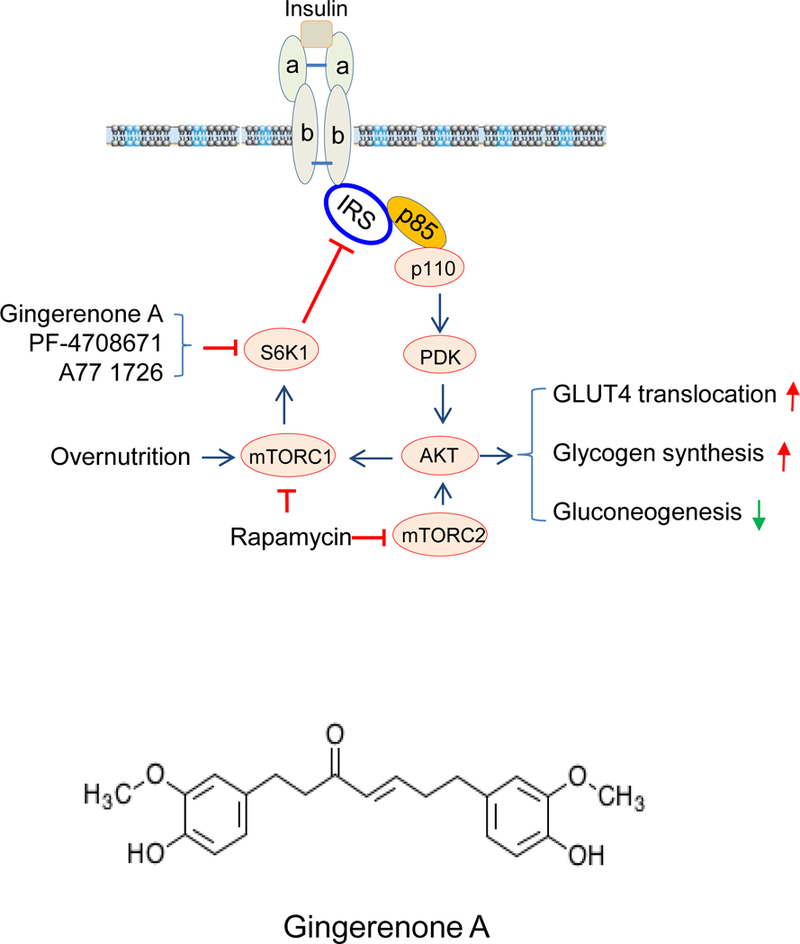
(A) Mode of action of Gin A and two other S6K1 inhibitors, PF-4708671 and A77 1726. Overnutrition with high concentrations of fatty acids and amino acids leads to constitutive S6K1 activation, which phosphorylates IRS-1S1101, leading to poor AKT activation. S6K1 inhibitors such as Gin A inhibit S6K1 activity and subsequently inhibit IRS-1S1101 phosphorylation, resulting in better interaction with the p85 subunit of PI3K and AKT activation. Activated AKT stimulates GLUT4 membrane translocation and glycogen synthesis but decreases gluconeogenesis. Chronic use of rapamycin leads to inhibition of both mTORC1 and mTORC2, thus exacerbating hyperglycemia. (B) Chemical structure of Gin A.
