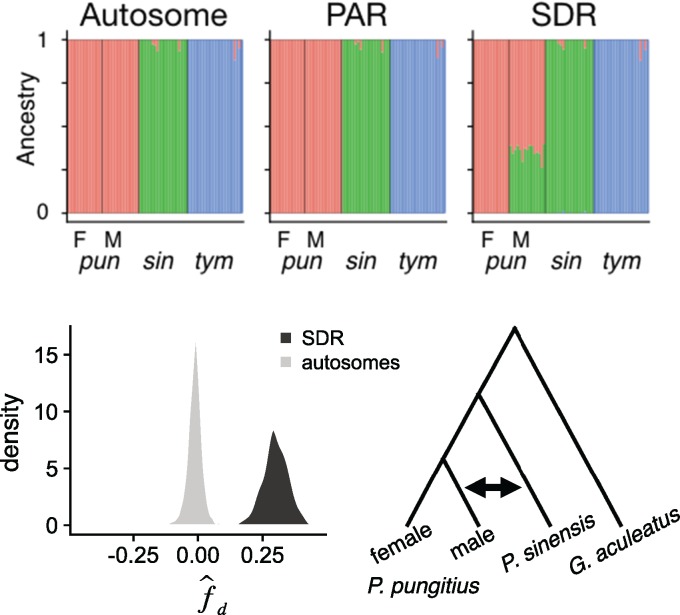
Fig. 3.
Shared ancestry P. pungitius males and P. sinensis. (Top): Admixture plots for an autosome (Chr 1), and the PAR and SDR from Chr 12 with female (F) and male (M) Pungitius pungitius separated. The three species are genetically distinct in the autosome and PAR. But in the SDR, P. pungitius males share about equal ancestry with P. pungitius females and P. sinensis. The ancestry that males share with females represents the X chromosomes, while that shared with P. sinensis represents the Y chromosomes. (Bottom): d statistic (ABBA-BABA) supports introgression specifically between P. sinensis and P. pungitius males. d was calculated for 100-kb windows across the genome, testing for excess of shared derived alleles between P. sinensis and P. pungitius males relative to P. pungitius females. The distribution for windows taken from the SDR (from 4 to 17 Mb) is shown in black (mean = 0.30). The distribution for equivalent regions from the autosomes is shown in gray (mean=−0.01).