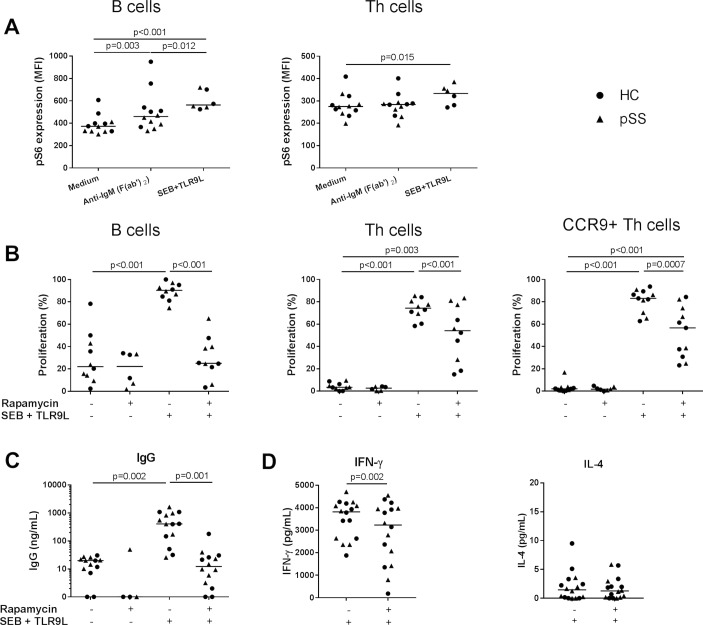
Figure 3.
B cell and T cell proliferation and production of IgG and IFN-γ are inhibited by mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) targeting in vitro. (A) B cell receptor cross-linking results in increased mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) activation (phosphorylation of S6) in B cells. Activation of T cells, including CCR9+ Th cells and B cells by a combination of superantigen SEB and TLR9-ligand CpG-C induces mTORC1 activation and is associated with proliferation of these cells (B) and IgG (C) and IFN-γ production (D), which is inhibited by rapamycin (100 nM). For all graphs: healthy controls (HC, circles), patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS, triangles). Medians are shown. IFN-γ, interferon gamma; IL, interleukin; SEB, Staphylococcal enterotoxin B; Th, T helper.