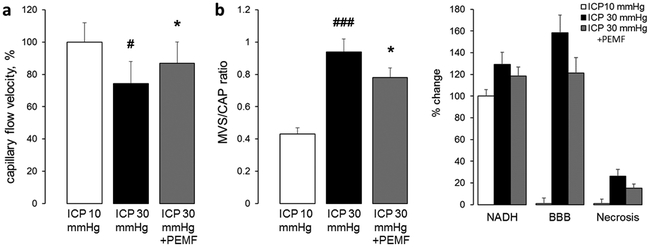
Figure 1.
High frequency pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation enhances capillary flow velocity (a); reduces microvascular shunt/capillary flow ratio (b); and attenuates tissue hypoxia, blood brain barrier damage and necrosis of neurons caused by four hours of intracranial hypertension (ICP=30 mmHg). Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n=10 rats per group, #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001 from a baseline of ICP=10 mmHg, *p<0.05, **p<0.01 from sham-treated group.