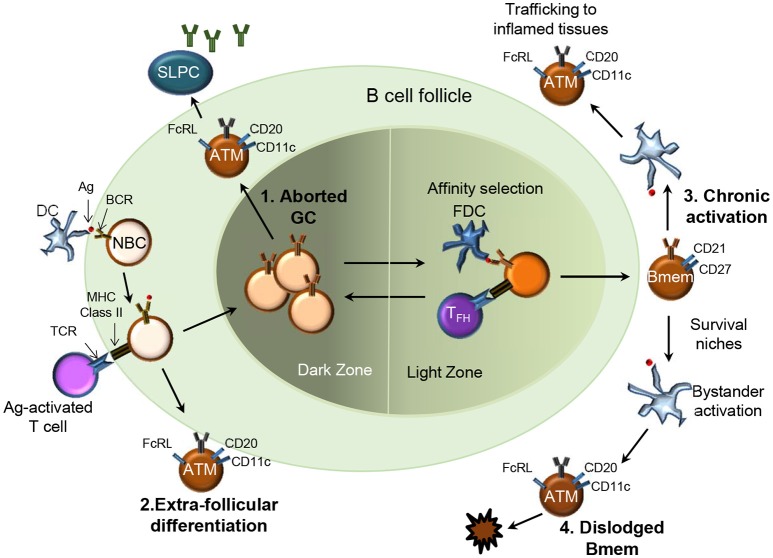
Figure 2.
Four potential pathways for generation of atypical memory B cells in chronic infections. Several pathways for the origin of atypical Bmem (ATM) have been proposed: 1.They may be Bmem derived from prematurely aborted GCs (top left), 2. Bmem derived from an extra-follicular differentiation pathway (bottom left); 3. Chronic Ag-mediated activation of previously functional Bmem may drive the expansion of ATM (top right), or 4. Represent the end stage for Bmem dislodged from survival niches due to repeated bystander activation (bottom right).