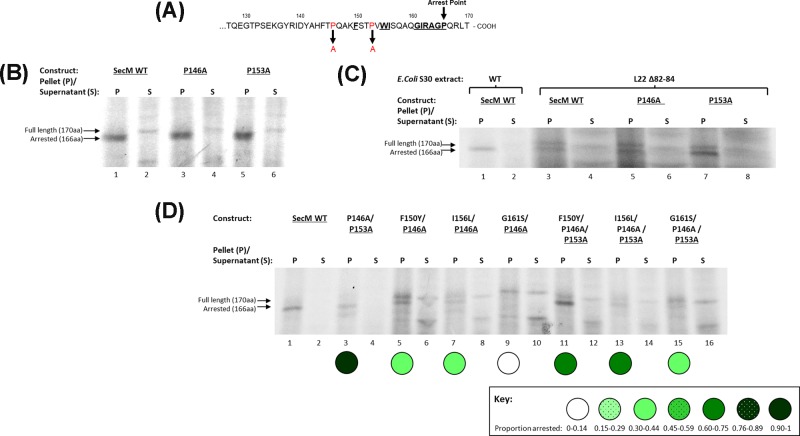
Figure 2. Effect of increased flexibility of SecM nascent chain within and out with the arrest motif on translation arrest.
(A) Schematic diagram indicating the position of the P146A and P153A mutations (highlighted in red) introduced into SecM constructs. The key arrest residues are highlighted in bold and underlined and the arrest point, Pro166, is indicated by an arrow. (B) SecM WT (lanes 1,2), P146A (lanes 3,4) and P153A (lanes 5,6) were translated in vitro and CTABr precipitated, separated into pellet (P) and supernatant (S) fractions and resolved by SDS/PAGE. (C) The constructs indicated were translated in coupled in vitro transcription–translation assays containing wild-type E. coli S30 cell extract (lanes 1,2) or cell extract derived from E. coli strain containing ribosomal deletion mutations of residues 82–84 of the L22 protein (lanes 3–8), which results in an expanded exit tunnel. The reactions were precipitated by CTABr, separated into pellet (P) and supernatant (S) fractions and resolved by SDS/PAGE. (D) SecM WT, P146A/P153A double mutant, double conservative mutations coupled with P146A and triple conservative mutations coupled with both P146A and P153A mutations were translated in vitro and CTABr precipitated, separated into pellet (P) and supernatant (S) fractions and resolved by SDS/PAGE.