Figure 5.
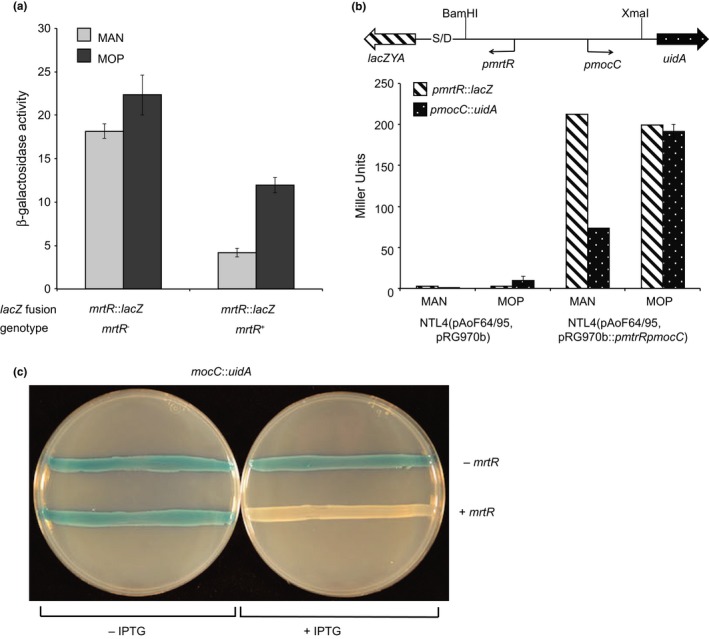
Expression of mocC is inducible by MOP and MrtR represses the mocC promoter. (a) The expression of mrtR was assessed using both transcriptional (n = 2, standard deviation) and translation (n = 3, standard deviation) lacZ fusions to the gene on pAoF64/95. Creation of the transcriptional fusion resulted in an intact copy of the target gene, while the translational fusion disrupted the gene of interest. Each strain was assessed for β‐galactosidase activity when grown in AB minimal medium with either mannitol (light gray) or mannopine (dark gray) as the primary source of carbon. Expression from the mrtR and mocC promoters was assessed using pRG970b::pmrtRpmocC, which contains the mrtR‐mocC intergenic region cloned into the bidirectional reporter plasmid pRG970b such that the mocC promoter is fused to uidA and the mrtR promoter is fused to lacZ (n = 1, error bars represent the standard deviation of the two internal replicates) (b). The strains harboring pAoF64/95 and this reporter plasmid were grown with either mannitol (MAN) or mannopine (MOP) and assessed for both β‐galactosidase and β‐glucoronidase activities as described in Experimental Procedures (b). The influence of MrtR on transcription of the mocC promoter was assessed using strain NTL4(pRG970b::pmrtRpmocC, pSRKGm::mrtR) and as a control NTL4(pRG970b::pmrtRpmocC, pSRKGm) (c). Strains were streaked on ABM medium containing X‐gluc with (right plate) or without (left plate) the addition of 0.1 mmol/L IPTG
