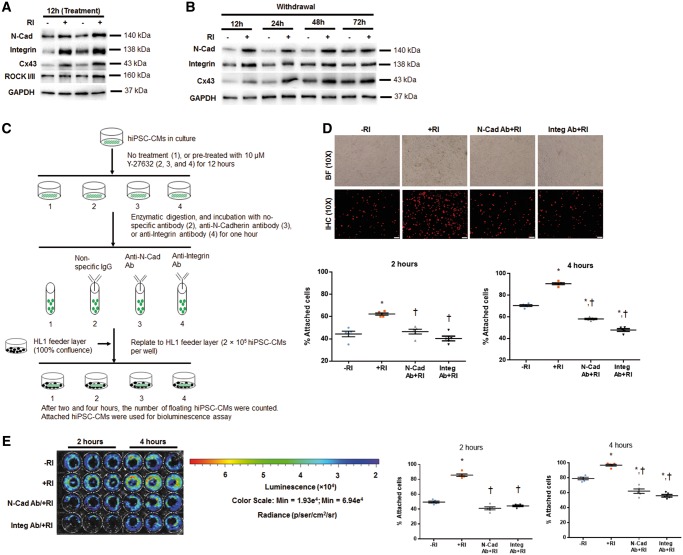
Figure 7.
Y-27632 enhances adhesion of hiPSC-CMs via promoting formation of adherens junctions. (A and B) Western blot data confirmed the upregulated expression of N-Cadherin, Integrin ß1, and Cx43 in hiPSC-CMs+RI at 12 h after cell passaging (relative to GAPDH) (A), and these differences were gradually normalized at 48–72 h after RI withdrawal (B). n = 5 replicates per group (A and B). Y-27632 preconditioning increases adhesion of hiPSC-CMs to the feeder layer, and this effect was partially abolished by pretreatment of CMs with anti-N-Cadherin or anti-Integrin ß1 antibodies. (C) Schematic representation of the adhesion experiment. (D) Immunofluorescence analysis of −RI and +RI hiPSC-CMs with and without their pretreatment with anti-N-Cadherin (N-Cad) and anti- and Integrin ß1 (Integ) antibodies. Attached hiPSC-CMs at 2 and 4 h after cell replating onto HL1 feeder layer were identified by immunostaining for hcTnT. The cell attachment rate was calculated by dividing the number of CMs attached to the feeder layer by the total number of CMs originally plated and expressed as a percentage. Bar = 100 µm. (E) Bioluminescence analysis of luciferase-expressing CMs treated as in D, and quantification of the attached cells (expressed as a percentage of total number of replated CMs), based on BLI signal quantification performed at 2 and 4 h time points; n = 5–7 replicates per group (D and E). *P < 0.05 vs. hiPSC-CM−RI; †P < 0.05 vs. hiPSC-CM+RI. One-way ANOVA analysis with Bonferroni correction was performed (D and E). Data were presented as the mean ± SEM.