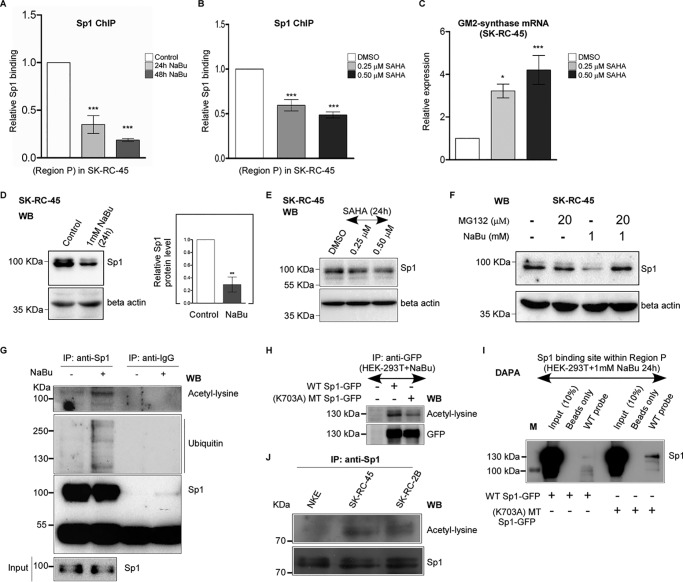
Figure 5.
Butyrate and SAHA induce loss of Sp1 binding with Region P of GM2-synthase gene. A, butyrate treatment reduces Sp1 binding at Region P of GM2-synthase gene. ChIP assay performed with SK-RC-45 cells treated with 1 mm NaBu at mentioned time points using antibody specific for Sp1. Precipitated chromatin DNA was estimated by qPCR. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. of three independent determinations for Region P (average ± S.E.; Student's t test; ***, p < 0.001). B, SAHA treatment reduces Sp1 binding at Region P of GM2-synthase gene. ChIP assay performed with SK-RC-45 cells treated with SAHA at mentioned concentrations for 24 h using antibody specific for Sp1. Precipitated chromatin DNA was estimated by qPCR. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. of three independent determinations for Region P (average ± S.E.; Student's t test; ***, p < 0.001). C, SAHA treatment in SK-RC-45 cells increases GM2-synthase transcription. SK-RC-45 cells were treated with SAHA at mentioned concentrations for 24 h. Total RNA was isolated and reverse-transcribed. cDNAs were subjected to qPCR using GM2-synthase primer. Relative expression values were normalized to the housekeeping gene GAPDH transcripts levels and represented as -fold change with respect to DMSO-treated cells as vehicle control. The data represent three independent determinations (average ± S.E.; Student's t test; *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001). D, NaBu treatment on SK-RC-45 cells down-regulates endogenous Sp1 protein expression. SK-RC-45 cells were treated with 1 mm NaBu for 24 h, and cell extracts were prepared followed by Western blot analysis with antibodies against Sp1 and β-actin. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. of four independent determinations (average ± S.E.; Student's t test; **, p < 0.01). WB, Western blotting. E, SAHA treatment on SK-RC-45 cells down-regulates endogenous Sp1 protein expression. SK-RC-45 cells were treated with SAHA at mentioned concentrations for 24 h, and cell extracts were prepared followed by Western blot analysis with antibodies against Sp1 and β-actin. F, MG132 treatment on SK-RC-45 cells blocks NaBu-mediated down-regulation of Sp1 protein. SK-RC-45 cells were treated with 1 mm NaBu for 24 h, and 20 μm MG132 was added 16 h post NaBu treatment and incubated for remaining 8 h, following which cell extracts were prepared for Western blotting analysis with antibodies against Sp1 and β-actin. G, Sp1 protein in SK-RC-45 cells treated with 1 mm NaBu for 16 h is ubiquitinated and acetylated. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated (IP) with antibodies specific for Sp1 or normal IgG. Immunocomplexes and input were probed with ubiquitin, pan-acetyl-lysine and Sp1 antibodies. H, mutated Sp1 protein (K703A) shows reduced acetylation compared with WT-Sp1 protein in presence of NaBu. Cell extracts from untransfected HEK-293T or transfected with indicated Sp1 plasmids tagged with GFP were immunoprecipitated (IP) with antibodies specific for GFP. Immunocomplexes were probed with pan-acetyl-lysine and GFP antibodies. I, acetylated WT-Sp1 protein binds less to the Sp1-binding site within Region P of GM2-synthase gene compared with less-acetylated (K703A) mutated Sp1 protein in vitro. DAPA with cell extract of HEK-293T cells which were transfected with either WT-Sp1 or K703A MT-Sp1 plasmids were incubated with 22-bp biotinylated probe encompassing the Sp1-binding site within Region P of GM2-synthase gene (WT probe). Proteins bound to the biotinylated probes were pulled down by streptavidin beads and probed for Sp1 protein using anti-Sp1 antibody by immunoblotting. The molecular mass of over-expressed Sp1 which is tagged with GFP is 125 KDa (Fig. S3B). Beads only panel was included as a negative control. M denotes protein marker. J, Sp1 protein in RCC cell lines shows higher acetylation compared with NKE. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated (IP) with antibody specific for Sp1. Immunocomplexes were probed with pan-acetyl-lysine and Sp1 antibodies.