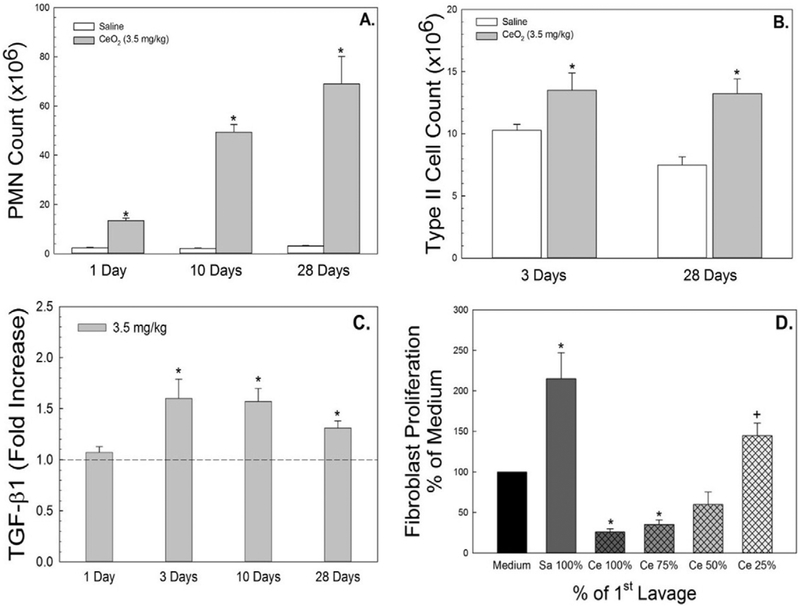
Fig. 1.
Effects of CeO2 (3.5 mg/kg) exposure on pulmonary inflammation and fibrotic cytokine secretion. PMN infiltration in BAL fluid and increased ATII cells isolated from lung tissues of CeO2-exposed rats at different time points after exposure were demonstrated in panel A and B, respectively. AM were harvested from control or CeO2-exposed rats and cultured ex vivo. TGF-β1 (C) was measured in the AM-conditioned supernate using ELISA. The effect of first BALF from control or CeO2-exposed rats on proliferation of fibroblasts from naïve rats were monitored. The BALF was used with no dilution as 100% or at 75%, 50% or 25% concentration of the CeO2-exposed BALF (D). The values are expressed as means ± SE, n = 6. *Significantly different from saline controls, p < 0.05. +Significantly different from the previous dilution, p < 0.05. The dotted line indicates control.