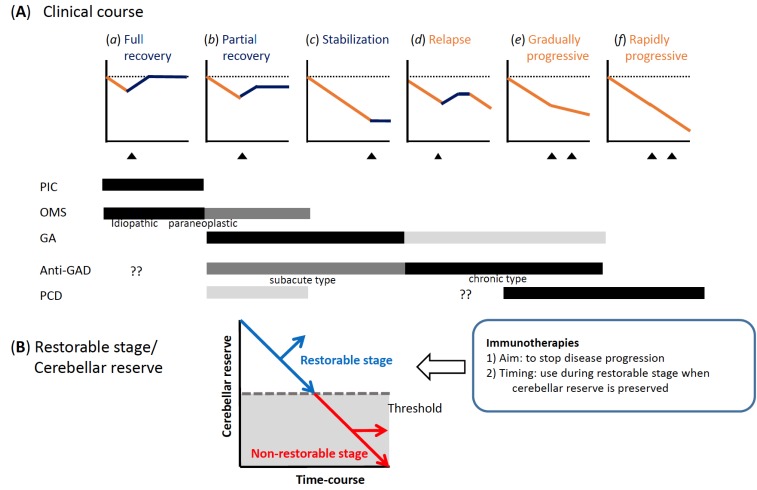
Fig. (2).
(A) Clinical time-course is classified into six patterns; (a) full recovery type, (b) partial recovery type, (c) stabilization type, (d) relapse type, (e) gradually progressive type, and (f) rapidly progressive type. Triangles: time of commencement of immunotherapy. Possible clinical courses for each subtype are schematically indicated below. Black: common course, gray: occasional course, light gray: rare course. PCI: post-infectious cerebellitis, OMS: opsoclonus myoclonus syndrome, GA: gluten ataxia, PCD: paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration, Anti-GAD: anti-GAD65Ab-associated CA. (B) Schematic diagram of decline of cerebellar function and the concept of “restorable stage” and “cerebellar reserve”. Proper therapies can restore cerebellar function in patients with the cerebellum at the “restorable stage”, meaning the presence of sufficient cerebellar functional reserve. (The color version of the figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).