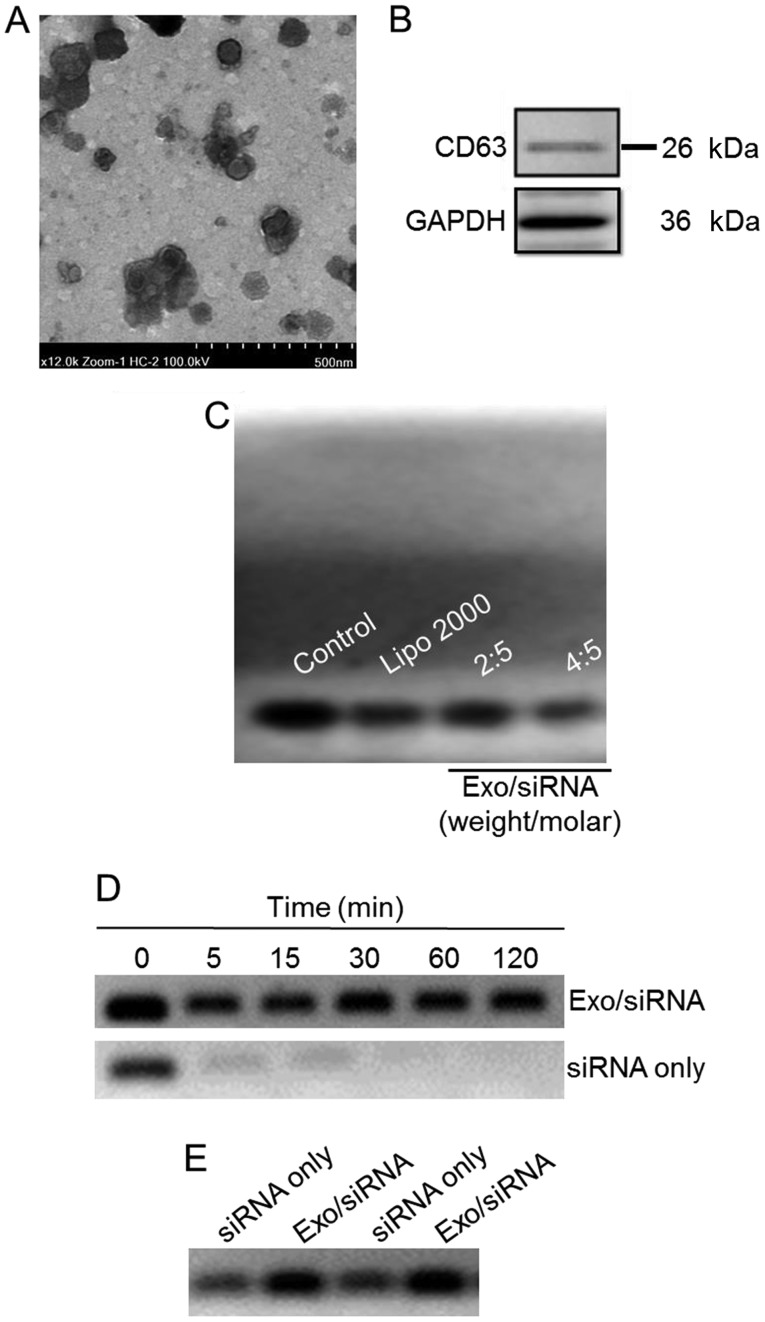
Figure 1.
Characterization of the exosome/TRPP2 siRNA complexes. (A) Representative transmission electron microscopy image displaying exosome/TRPP2 siRNA particles counterstained with 4% uranyl acetate. Scale bar, 500 nm. (B) Representative image presenting the protein expression of CD63, an exosomal marker. (C) Exosomes encapsulated TRPP2 siRNA (Exo/siRNA) in a concentration-dependent manner. The TRPP2 siRNA packaging capacity of exosomes was assessed. An agarose gel retardation assay was performed at different weight/molar ratios of exosomes to TRPP2 siRNA (µg/nM; Exo/siRNA). (D) Stability of TRPP2 siRNA only and TRPP2 siRNA encapsulated within exosomes against enzymatic degradation following incubation with RNA nucleases for 0, 5, 15, 30, 60 and 120 min or (E) in serum for 120 min in a 4:5 ratio of exosomes to TRPP2 siRNA (µg/nM) or naked siRNA (siRNA only). In the Exo/siRNA group, heparin was added to the exosome/TRPP2 complexes to release TRPP2 siRNA prior to conducting the gel retardation assay. Exo, exosome; Lipo, Lipofectamine®; CD, cluster of differentiation; siRNA, small interfering RNA; TRPP2, transient receptor potential polycystic 2; Exo, exosome.