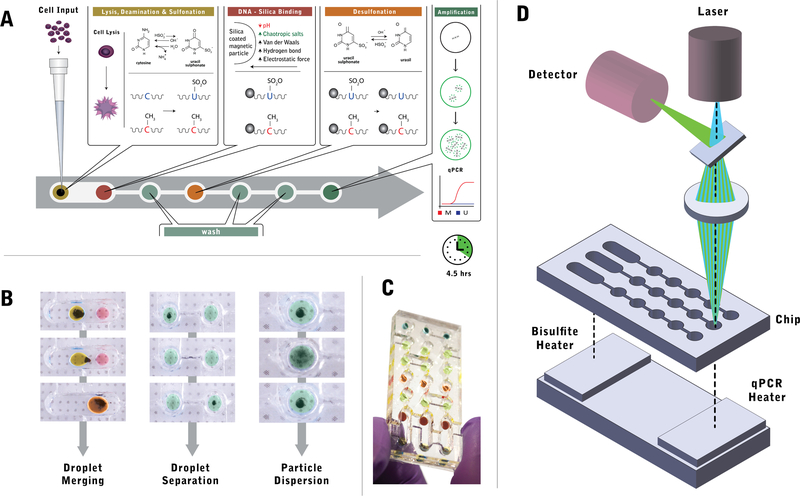
Fig. 1.
Overview of the droplet magnetofluidic platform for fully integrated methylation analysis. a Quantitative MSP assay protocol on chip. A liquid suspension of human cells is directly loaded into the first chamber, where it is merged with a droplet containing magnetic particles and bisulfite conversion reagent for cell lysis and bisulfite conversion. The droplet is subsequently merged with a second reagent droplet to facilitate DNA binding on magnetic particles. Subsequent steps involve desulphonation and DNA elution, which are each preceded by a series of wash reagents to ensure minimal carryover of upstream buffers and other contaminants. Upon elution into the PCR reagent in the last well, methylation marker quantification is performed directly on chip via quantitative PCR. The entire process is completed in 4.5 h. b Droplet operations on chip. Magnetofluidic control enables three operations: droplet merging, droplet separation and particle dispersion. Droplet merging facilitates additive operations by taking advantage of the operating regime where capillary force on an actuated magnetic particle is less than the magnetic force on the particles. Droplet separation utilizes a sieve structure on the chip to maximize capillary force, thereby facilitating dissociation of the magnetic particle from the reagent droplet. Particle dispersion is achieved when magnetic field is removed from the chip, resulting in the release of particle plug into a dispersed plume. c Photograph of the assembled chip containing aqueous droplets mixed with food dye for visualization. d The MSP chip operates in tandem with a thermal control unit, consisting of two heating blocks for bisulfite conversion and thermal cycling. The chip interfaces on its top surface with a fluorometer, which acquires real-time signal from the droplets during PCR