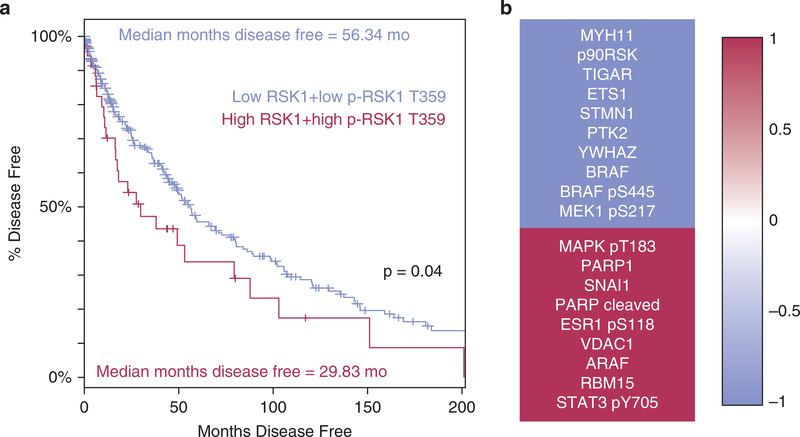
Figure 6. p90RSK is a potential clinical therapeutic target in BRAF-mutant melanoma.
(a) Patients indexed in The Cancer Genome Atlas were stratified into high and low RSK1 expressers, P = 3.9 × 10−7 patients with high p90RSK levels (n = 36) showed 26.5-month poorer disease-free survival versus patients who were low for both (n = 272), Kaplan-Meier estimate, P = 0.04. (b) RPPA screening of levels of 217 proteins in lysates collected from seven BRAF-mutant drug-naïve melanoma lines showed significant, P < 0.05, positive, and negative interaction between 20 proteins and BI-D1870 GI50. The top 10 genes with the strongest negative correlation of protein levels to drug potency are shown in red, whereas those with the strongest positive correlation between protein levels and drug potency are shown in blue. MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MEK, MAPK/ERK kinase; p90RSK, p90 subfamily of ribosomal S6 kinase; RPPA, reverse phase protein array; RPS6, ribosomal protein S6.