Figure 3. Physiological effects of NAD-boosting molecules.
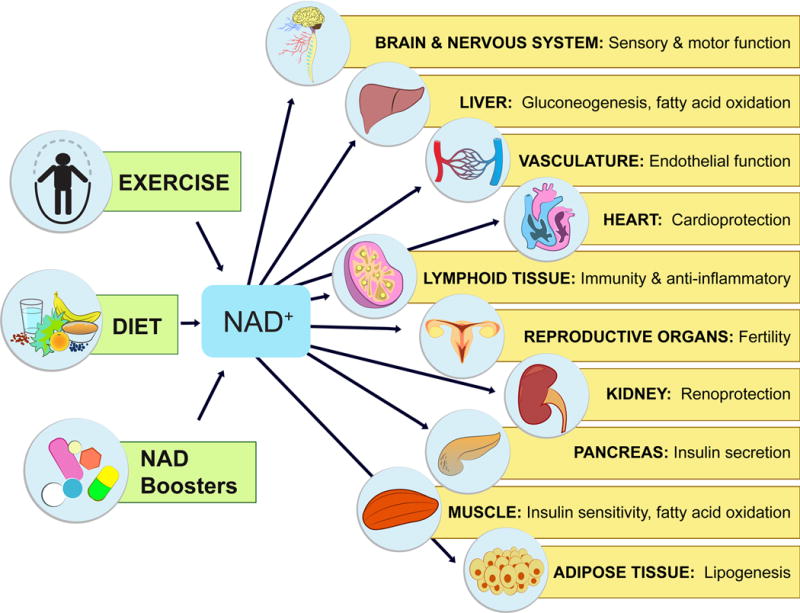
NAD+ levels steadily fall as we age, leading to a decline in the function of cells and organs. By raising NAD+, NAD+ boosters can have profound effects on the health and survival of mammals. Increases in NAD+ promote cognitive and sensory function, gluconeogenesis in liver, lipogenesis in adipose tissue, insulin secretion in pancreas, and insulin sensitivity in muscle. NAD+ also promotes endothelial cell proliferation and protects against cardio- and cerebrovascular disease. NAD regulates immune function and inflammation and, protects against acute injury in kidney. NAD promotes and extends fertility in both males and females, ostensibly by activation of sirtuins.
