Figure 4. Potential impact of NAD+ boosters on human health via NAD+ signaling pathways.
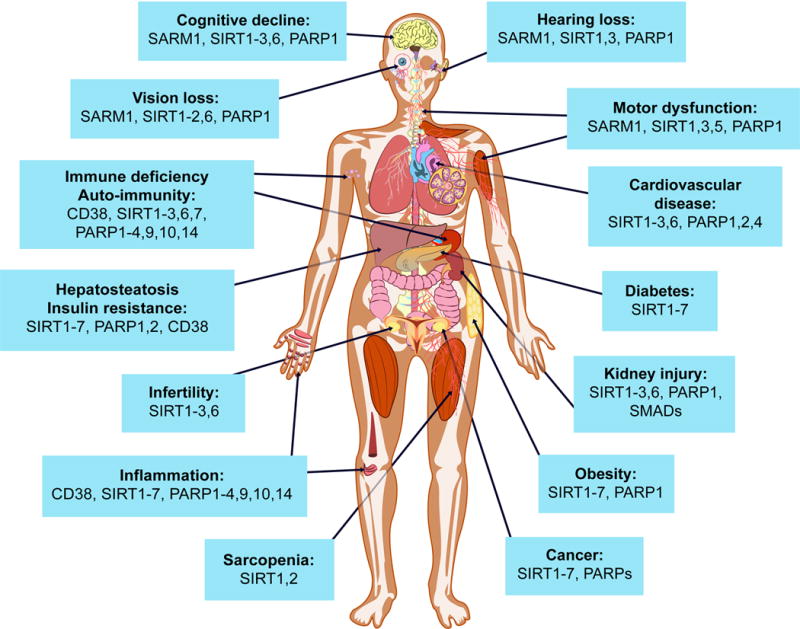
A decline in NAD+ during aging is believed to be a major cause of disease and disability, such as hearing and vision loss, as well as cognitive and motor dysfunction, immune deficiencies, auto-immunity and dysregulation of the inflammatory response leading to arthritis, metabolic dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. In mouse models, NAD+ boosters prevent or treat a variety of different diseases, prompting a search for NAD+ boosters that are safe and effective as drugs to treat both rare and common diseases, and potentially aging itself.
