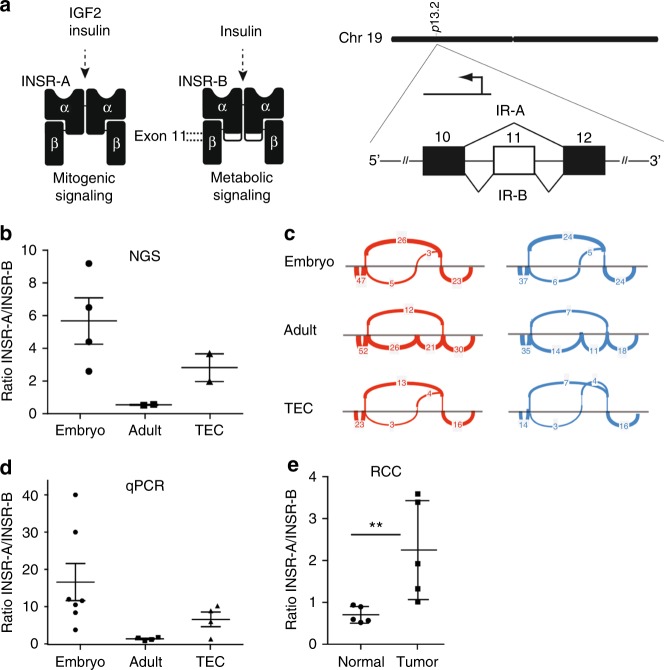
Fig. 2.
Insulin receptor variant A (INSR-A) is the main splice variant present in tumour endothelial cells. a Schematic representation of the two splice variants of INSR, INSR-A (lacking exon 11) and INSR-B (full-length protein). The isoforms differ in ligand affinity and cellular downstream signalling.14 b, c RNA sequencing and variant analysis show the relative ratio of INSR-A over INSR-B in isolated tumour endothelial cells (TEC), mouse embryo and adult mouse, and point to a dominant role for INSR-A in TEC and embryo compared to the adult mouse (ratio INSR-A/INSR-B »1). This is visualised in sashimi plots (c), showing that in TEC and embryo the preferential isoform is INSR-A in which exon 11 is omitted. The main variant present in the adult mouse is INSR-B, in which exon 11 is included. d Expression of the different splice variants analysed by qPCR confirms these observations. e Ratio of INSR-A to INSR-B expression in human renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and healthy kidney tissues, determined by qPCR. **P < 0.01 by Mann–Whitney test, N = 5