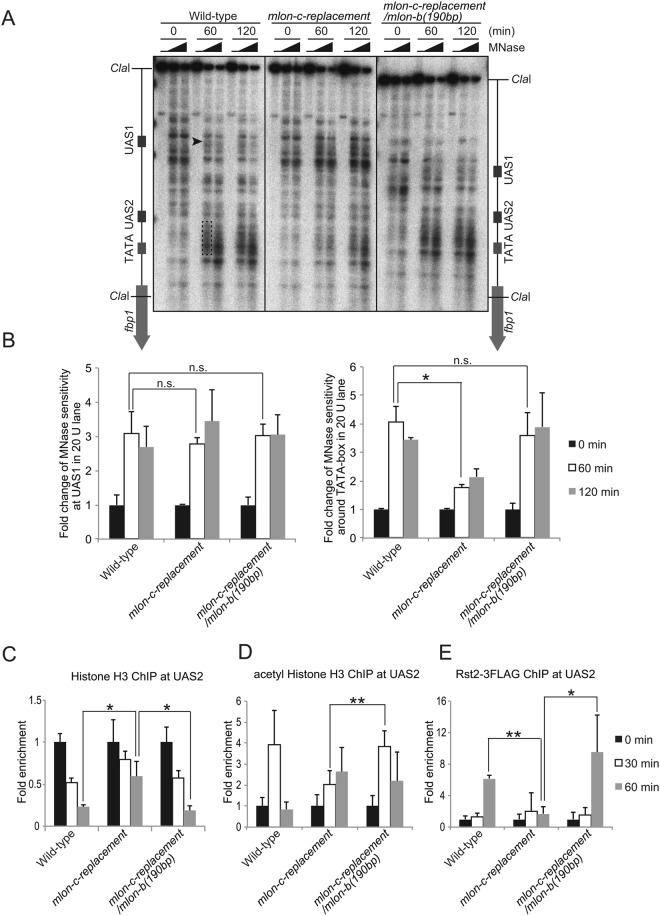
Figure 3.
mlonRNA-b transcriptional initiation 190 bp upstream from UAS2 bypasses the requirement of mlonRNA-c transcriptional initiation for the efficient chromatin remodeling and transcription-factor binding. (A) Southern blot image showing MNase sensitive sites around the fbp1 promoter in the indicated cells cultured in YED for the indicated time. The isolated chromatin was digested with 0, 20, or 50 units/ml of MNase at 37 °C for 5 min. Purified DNA was digested with ClaI and analyzed by Southern blotting. Black arrowhead indicates region with MNase-sensitive sites at UAS1. Dotted line indicates MNase-sensitive sites around UAS2-TATA box. (B) Histogram shows the quantification of MNase-sensitive bands in the UAS1 (Black arrowhead) and UAS2-TATA box region (Dotted line). The error bars show the standard deviation from at least two independent experiments. (C–E) ChIP analysis to examine histone binding (C), histone acetylation (D) and Rst2 binding (E) at UAS2 in wild-type, mlon-c-replacement, and mlon-c-replacement/mlon-b(190 bp) cells. The relative increase in the ratio at the indicated time after glucose starvation is indicated. Error bars represent standard deviations from at least two independent experiments. p-value was calculated by a Student’s t-test: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and n.s. (not significant, p > 0.05).