Figure 2.
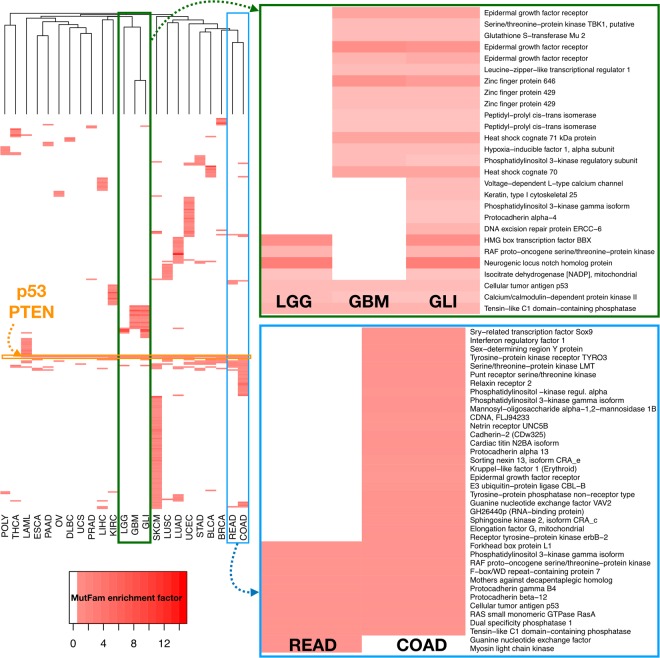
Heatmap shows overall diversity of functions affected in different cancers and clustering of certain cancers by primary tumour site. Each horizontal bar represents a MutFam, with enrichment factors shown using colour intensity. MutFams that include tumour suppressor genes TP53 and PTEN are shared amongst the largest number of cancers. Tumours from the same primary site that cluster by their MutFams are shown in more detail for gliomas (top right) and colorectal cancers (bottom right) and include the CATH Functional Family names. For gliomas, MutFams include genes TP53, PTEN and CHEK2 found in all three subtypes (LGG, GBM and GLI), with genes such as EGFR and ZNF429 found only in GLI and late stage GBM. For colorectal cancers, common MutFams include TP53, PTEN, KRAS, PIK3CA and the F-box/WE repeat containing FBXW7, with COAD containing many unique MutFams including genes EGFR, NRAS and relaxin receptor 2 (TSHR). (A) full list of MutFams in given in Supplementary Table 2. BLCA Bladder cancer; BRCA Breast invasive carcinoma; COAD Colon adenocarcinoma; DLBC Lymphoid Neoplasm Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma; ESCA Esophageal carcinoma; GBM Glioblastoma multiforme; GLI Gliomas; KIRC Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; LAML Acute Myeloid Leukemia; LGG Low grade gliomas; LIHC Liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD Lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC Lung squamous cell carcinoma; OV Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma; PAAD Pancreatic adenocarcinoma; PRAD Prostate adenocarcinoma; READ Rectum adenocarcinoma; SKCM Skin Cutaneous Melanoma; STAD Stomach adenocarcinoma; THCA Thyroid carcinoma; UCEC Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma; UCS Uterine Carcinosarcoma; POLY Polymorhisms (neutral mutations).