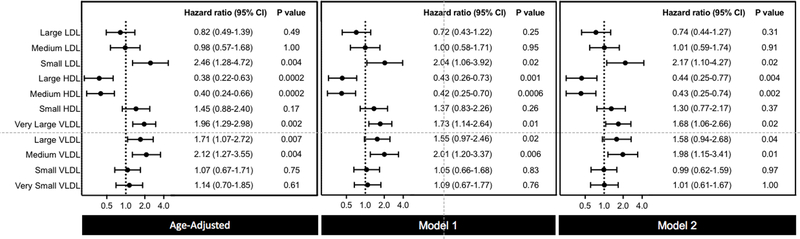
Figure 3. Risk Associations Between NMR Lipoprotein Particle Subclasses and Incident PAD.
Hazard ratios and 95% CIs for the top versus bottom tertile of NMR lipoprotein particle subclasses. Model 1 adjusted for age and smoking pack-years. Model 2 adjusted for age, smoking pack-years, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, hormonal therapy, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, lipid lowering therapy, randomized treatment assignment, and body mass index.