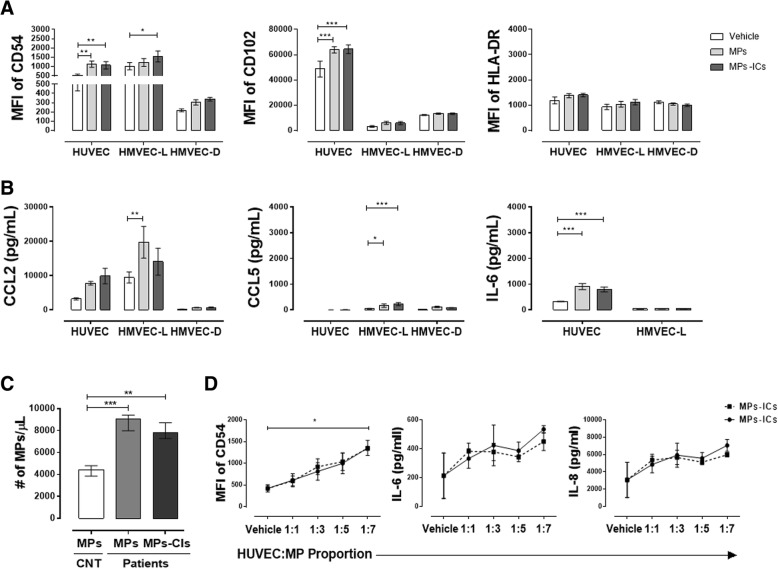
Fig. 2.
Microparticles (MPs) and microparticles that form immune complexes (MPs-ICs) from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) increased the expression of adhesion molecules and soluble factors in endothelial cells. a Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CD54, CD102, and HLA-DR in endothelial cells of the macrovasculature (human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC)) and microvasculature (human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HMVEC-L) and human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HMVEC-D)) without treatment (vehicle) and treated with MPs and MPs-ICs from patients with RA and SLE for 24 h. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. Two-way analysis of variance, *p ≤ 0.05, f2:8 **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, n = 6–8. Accumulation of the chemokines b CCL2, CCL5, and the cytokine IL-6 in supernatants of HUVEC, HMVEC-L, and HMVEC-D treated with MPs and MPs-ICs. The white bar corresponds to cells without treatment (vehicle); the light gray bar corresponds to cells treated with MPs, and the bar corresponds to cells treated with MPs-ICs. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. Two-way analysis of variance, *p ≤ 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, n = 6–8. c Number of MPs and MPs-ICs per microliter obtained from healthy controls (HCs) and patients with RA and SLE and counted by flow cytometry. d MFI of CD54, levels of IL-6 and IL-8 in supernatants of HUVEC treated with different proportions (1:1, 1:3, 1:5, 1:7) of MPs (continuous black line) and MPs-ICs (broken black line) from patients with RA. Data are presented as the median ± interquartile range. Kruskal–Wallis, *p ≤ 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, n = 3–6