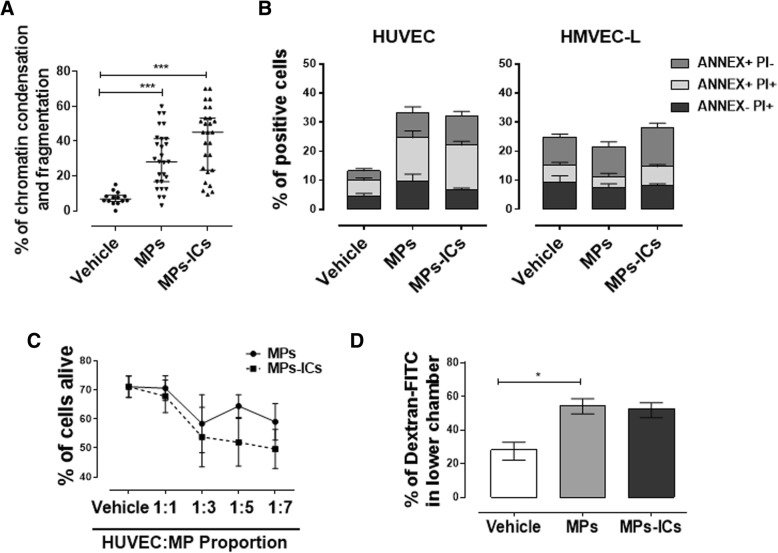
Fig. 5.
Microparticles (MPs) that form immune complex (MPs-ICs) from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) induced cell death and increased the monolayer permeability in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). a Percentage of chromatin condensation and fragmentation of HUVEC without treatment (vehicle) or cultured in the presence of MPs or MPs-ICs from patients with RA and SLE for 24 h; data were obtained from ≥ 5 different fields by each experimental condition by using a ×20 objective. Data are presented as the median ± interquartile range. Kruskal–Wallis, *p ≤ 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n = 3. b Percentages of annexin V − PI+ (ANNEX−PI+), annexin V+ PI+ (ANNEX+PI+) and Annexin V− PI+ (ANNEX+PI−) in HUVEC or human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HMVEC-L) after treatment with MPs and MPs-ICs are shown. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. Two-way analysis of variance, n = 4. c Percentage of living HUVEC after the treatment with different proportions (1:1, 1:3, 1:5, 1:7) of MPs (continuous black line) and MPs-ICs (broken black line) from patients with RA. Data are presented as the median ± interquartile range. Two-way analysis of variance, n = 3–6. d Percentage of dextran-FITC that crossed the HUVEC monolayer and was detected in the lower chamber after treatment with MPs and MPs-ICs. Data are presented as the median ± interquartile range. Kruskal–Wallis, *p ≤ 0.05, n = 4