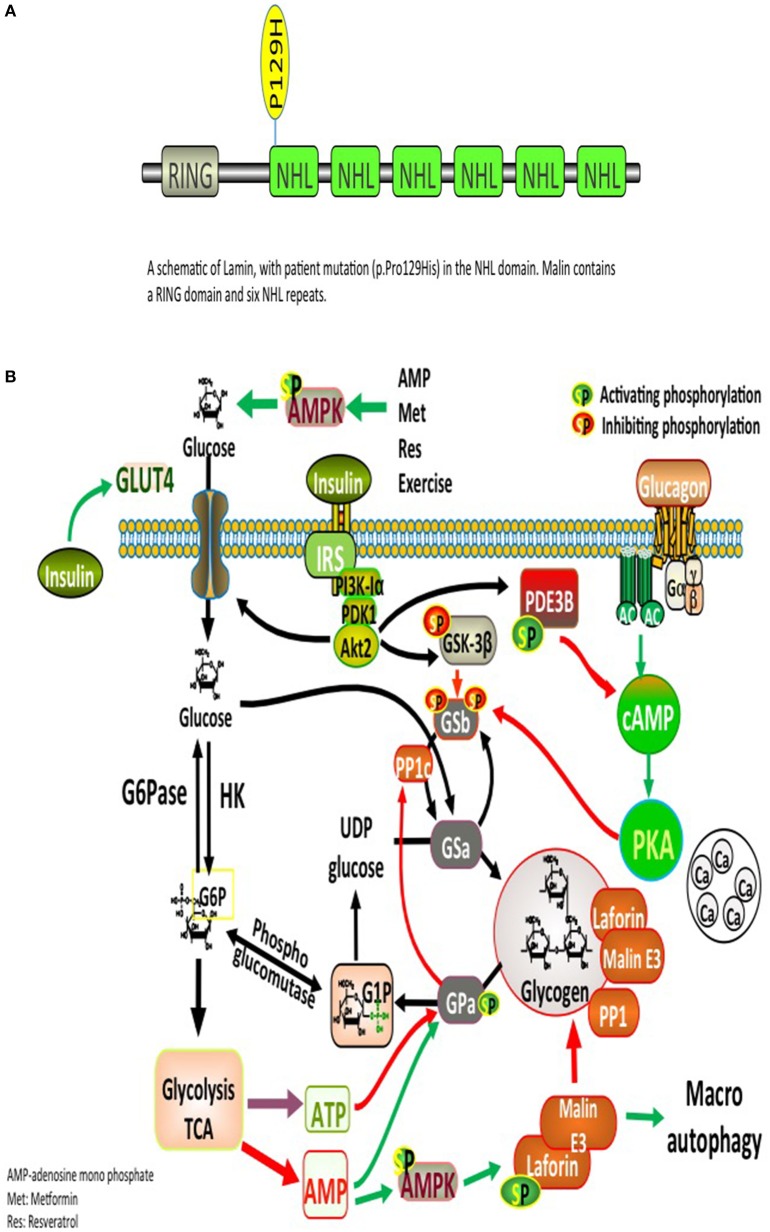
Figure 1.
(A) Glycogen metabolism, degradation, and glycogen-metabolizing protein interactions. Both insulin and exercise increase glucose uptake via GLUT4. Increased Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) levels provide feedforward activation of glycogen synthase (GS). HK, hexokinase; G6Pase, glucose-6-phosphatase; GNG, gluconeongenesis; PGM, phosphoglucomutase; GAA, lysosomal α-glucosidase; BE, branching enzyme; PH, glycogen phosphorylase; UP, UPD-glucose pyrophosphorylase; UGPPase, UDP-glucose pyrophosphatase; GN, glycogenin; GS, glycogen synthase; DBE, debranching enzyme; PKA, protein kinase A; LB, Lafora bodies (10). (B) A schematic illustration of Lamin structure with patient's mutation (p.Pro129His) in the NHL domain. Malin contains a RING domain and six NHL repeats.