Figure 2.
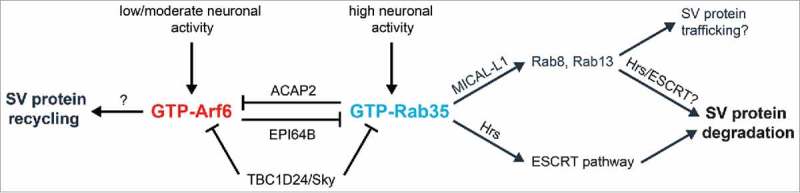
Putative pathway for antagonistic Rab35/Arf6 regulation in presynaptic terminals. Rab35 activation by high neuronal firing rates leads to Hrs binding, ESCRT pathway recruitment, and subsequent SV protein degradation as shown in Figure 1. Rab35 activation may also induce binding with its effector MICAL-L1, leading to the recruitment of additional Rab GTPases (Rabs 8 and 13) to catalyze downstream SV protein degradation and/or trafficking events. Finally, Rab35 activation may simultaneously inactivate Arf6 via ACAP2, a Rab35 effector and Arf6 GAP. On the other hand, Arf6 activation in response to low or moderate neuronal activity is hypothesized to promote SV protein recycling back to the readily-releasable pool, while inactivating Rab35 activity via EPI64B, an Arf6 effector and Rab35 GAP. TBC1D24/Sky may serve as a GAP for both Rab35 and Arf6. Additional work is needed to verify these pathways and determine the cellular signals responsible for Arf6 and Rab35 activation/inactivation at presynaptic terminals.
