Figure 4.
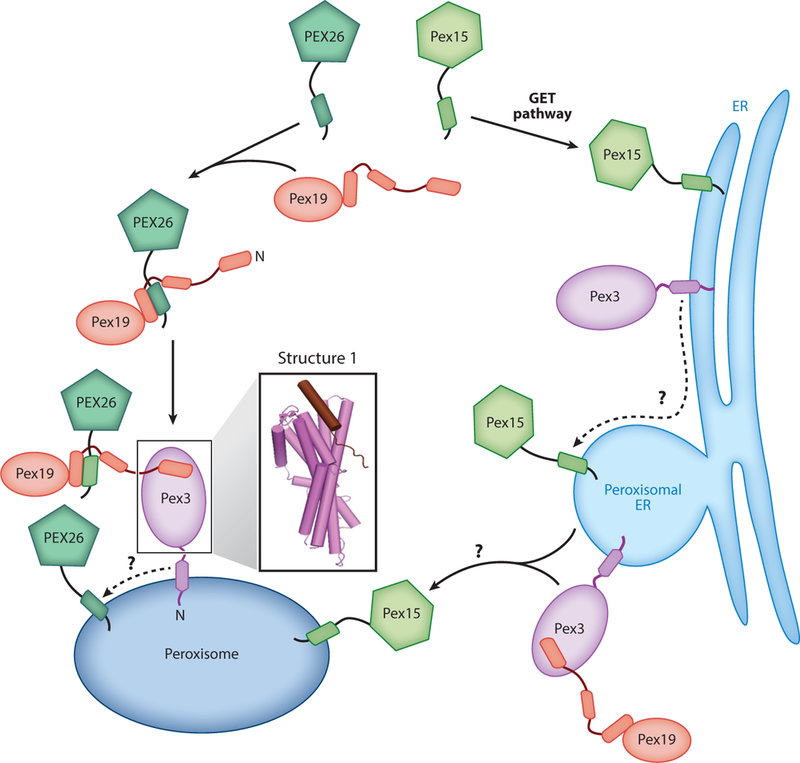
Two distinct pathways target tail-anchored proteins to peroxisomes. In the direct pathway (left path), Pex19 captures PEX26 in the cytosol and delivers it to peroxisomes via interaction with Pex3. PEX26 is then inserted into the peroxisomal membrane via an unknown mechanism. In the ER-dependent pathway (right path), Pex15 is first targeted to the ER membrane and is then sorted to peroxisomal ER. Exit of Pex15 from the ER occurs via budding of preperoxisomal vesicles that eventually fuse with peroxisomes, and this process requires Pex3 and Pex19. Structure 1 (PDB 3AJB) shows the crystal structure of the Pex3 cytosolic domain bound to the Pex19 N-terminal peptide.
