Figure 1.
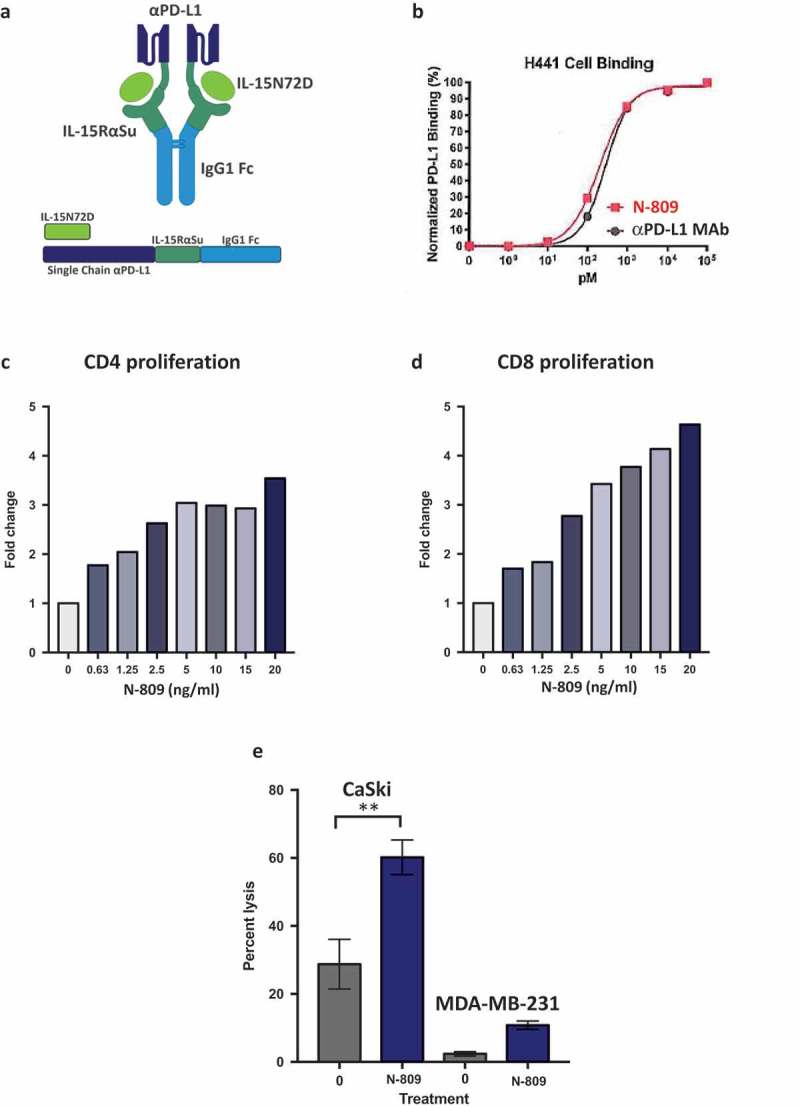
Schematic diagram of N-809, PD-L1 binding, and effects of N-809 on the proliferation and activity of CD4 and CD8 T cells. (a) Illustration of N-809, a bifunctional molecule created by fusing two single chain human anti-PD-L1 domains to an IL-15 superagonist scaffold with an IgG1 Fc portion. (b) Binding of N-809 to PD-L1+ H441 cells was analyzed by flow cytometry using APC labeled antibody specific for the Fc portion of hIgG. (c, d) Healthy donor CD4 and CD8 T cells were stimulated with plate-bound anti-CD3 and increasing concentrations of N-809. Fold change represents the change from untreated (0 ng/ml), anti-CD3 stimulated T cells for one representative donor. (e) Tumor cell lysis by an HPV E7-specific T cell line grown in the presence or absence of N-809 (37.5 ng/ml). Results of a lysis assay using CaSki (cervical carcinoma) cells as targets at a 10:1 E:T ratio is shown. MDA-MB-231 (breast carcinoma) cells were used as a control to determine specificity of the lysis. **P < 0.01.
