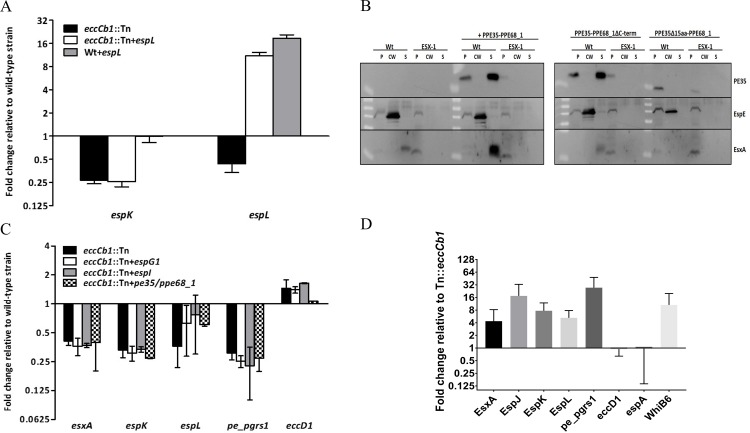
Fig 5. Regulation of the ESX-1 secretion system.
(A) Down-regulation of espL is the result of a regulatory process. A functional copy of espL was introduced into wild-type and eccCb1 mutant strains of M. marinum, and the espK and espL gene expression levels were measured by qRT-PCR. Gene expression levels were compared to those of the wild-type strain E11. Values represent mean ± standard error of the mean of two biological replicates. (B) Introduction of PE35/PPE68_1 result in increased EsxA secretion but not in gene regulation. Pellet (p), cell wall extract (cw), and supernatant (s) fractions of the wild-type and eccCb1 mutant strains of M. marinum expressing PE35/PPE68_1; PE35/PPE68, containing a C-terminal deletion of PPE68_1; or PE35/PPE68_1, containing a 15-amino-acid C-terminal deletion of PE35, were analysed for the presence of EspE, EsxA and the introduced PE35 by immunoblotting. Fractions represent 0.5, 1 or 2 OD units of original culture. In all cases, PE35 contained a C-terminal HA tag. (C) EspG1, EspI and PE35/PPE68_1 do not regulate the transcription of selected esx-1-associated genes. EspG1, EspI or PE35/PPE68_1 were overexpressed in the M. marinum eccCb1 mutant strain, and the expression levels of espK, espL, esxA, pe_pgrs1 and eccD1 were measured by qRT-PCR. Gene expression levels were compared to those of the wild-type strain E11. Values represent mean ± standard error of the mean of at least two biological replicates. (D) WhiB6 is involved in transcriptional regulation of ESX-1 substrates and associated genes. The whib6 gene was overexpressed in the M. marinum eccCb1 mutant strain, and transcript levels of espK, espL, esxA, pe_pgrs1 and eccD1 were measured by qRT-PCR. Gene expression levels were compared to those of the eccCb1 mutant strain. Values represent mean ± standard error of the mean of two biological replicates.