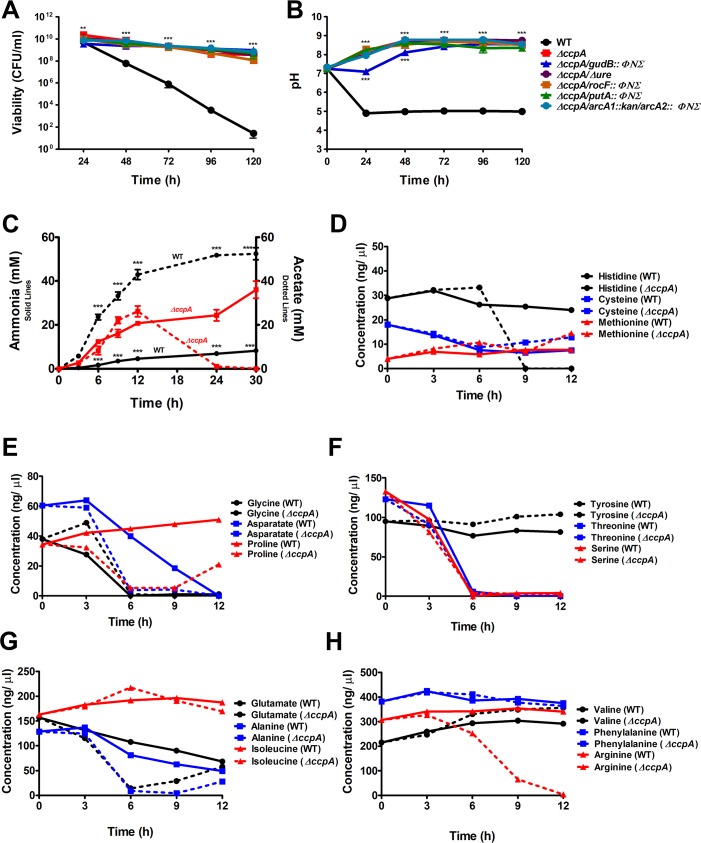
Fig 4. Loss of ccpA promotes survival under weak acid stress.
(A) and (B) Five-day growth assay of JE2 WT, JE2 ΔccpA, JE2 ΔccpA/gudB::ΦΝΣ, JE2 ΔccpA/Δure, JE2 ΔccpA/rocF::ΦΝΣ, JE2 ΔccpA/putA::ΦΝΣ, and JE2 ΔccpA/arcA1::kan/arcA2::ΦΝΣ, cultured in TSB containing 45 mM glucose. (A) Viability (CFU/ml) and (B) pH was monitored every 24 h (n = 3/strain, mean ± SEM). Statistical significance was assessed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test compared to JE2 WT at each timepoint; ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. (C)-(H) Growth assay of JE2 WT and JE2 ΔccpA cultured in TSB containing 45 mM glucose over 30 h. (C) Extracellular ammonia and acetate levels were measured at 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 24, and 30 h (n = 3/strain, mean ± SEM). Statistical significance was assessed using two-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni post-test; *** P < 0.001. (D)-(H) Amino acid analysis was performed with culture supernatants of both strains at 0, 3, 6, 9, and 12 h to determine the free amino acid concentrations (ng/μl). Amino acid analysis experiments performed with one replicate. WT is represented by solid lines and the ccpA mutant is represented by dotted lines.