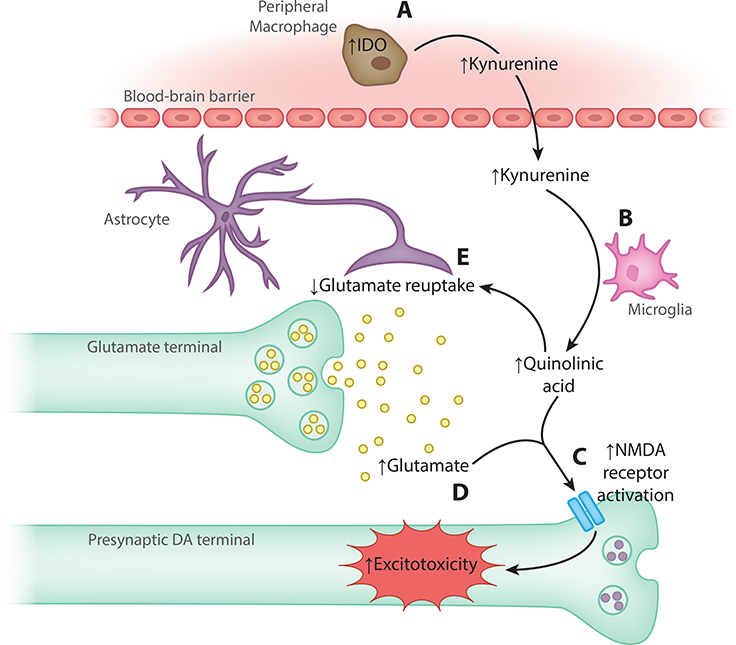
Figure 3. Inflammation-induced excitotoxicity through the kynurenine pathway.
(A) Pro-inflammatory cytokines stimulate indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) in peripheral macrophages, resulting in production of kynurenine that crosses the blood-brain barrier. (B) Microglia convert kynurenine to quinolinic acid (QUIN). (C) In turn, QUIN exerts possibly neurotoxic effects, in part by (D) activating N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, and (E) by decreasing glutamate reuptake, which increases glutamate release to potentially excitotoxic levels [106]. DA, dopamine; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; NMDA, N-methyl-d-aspartate.