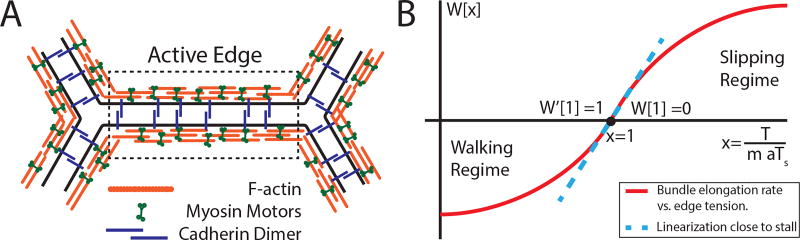
FIG. 2.
Role of myosin motors in the ATN model. (A) Schematic of the basic active element of a tension network: actomyosin cables on apposing interfaces are cross-linked by cadherin dimers; (B) Dependence of the actomyosin bundle contraction rate on mechanical load: the “walking kernel” W(x), see Eq. (3), changes sign from contraction to elongation when mechanical load per myosin T/am exceed the stall load Ts.